* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Review #2
Holliday junction wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid tertiary structure wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Alternative splicing wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
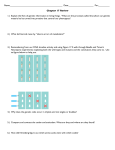
Molecular Biology Spring, 2011 This is the review sheet for the second exam. It covers chapters 10 through 13. Homologous recombination What are the details of the Holiday model of recombination? What are the steps? Which evidence does it agree with and which does it not? What is the double-strand break model of recombination? What are the steps? Which evidence does it agree with and which does it not? Which proteins in E. coli are involved in homologous recombination? What is the function of each of them? What are χ-sites and their function? How does homologous recombination occur in eukaryotes? What are the functions of the proteins involved? How do they relate to the E. coli proteins? How does mating type switching occur in Saccharomyces cerevisiae? What does the locus look like? How does the process differ from the DSB model? What is gene conversion? Site-specific recombination and transposition What is conservative site-specific recombination (CSSR)? What elements are found in the RS? How are the RS related to the types of rearrangements that occur by CSSR? What is the basic process for CSSR? What happens at each step? What are the two categories of recombinases? What are the basic features of serine recombinases? What is the process of how they recombine DNA? What are the basic features of tyrosine recombinases? What is the process of how they recombine DNA? What is the process for the Cre recombinase? How does λ integrate and excise from E. coli? What are the RS, what proteins are involved, and how do they carry out the processes? In Salmonella, the flagellin protein is controlled by recombination. How? What are the important features of the Hin region? Which proteins are involved? How do cells prevent dimers of chromosomes? Which proteins are involved? What are the steps in the process? What is transposition? What are transposons and transposable elements? What are the three major families of transposition? What are DNA transposons? What features do they have? What are the two types of transposons and what are their structures? What do viral-like retrotransposons and retroviruses look like? What proteins are required by them? What is the structure of poly-A retrotransposons? What is the mechanism of non-replicative transposition? What steps are involved and which proteins are necessary? What are the three methods that have been found for cleaving the “nontransferred” strands (5’ ends)? What is the process of replicative transposition? How does it differ from nonreplicative? What is the mechanism of viral-like retrotransposon movement? What steps are involved and which proteins are necessary? What are the similarities and differences of integrases and transposases? What is the mechanism of poly-A retrotransposon movement? What steps are involved and which proteins are necessary? What does Tn10 look like? How does it transpose? What affects its copy number? How and why does DNA replication affect its movement? 1 How do we generate huge number of antibodies and T-cell receptors? What is the structure of the antibody region? How do we join the V, D, and J segments? What protein(s) are involved? What is the mechanism of the recombination? Mechanisms of transcription What is the subunit structure of bacterial RNA polymerases? What is the 3D shape? What are the three phases of the process of making RNA, and what, in general, happens in each phase? What is the basic structure of the promoter, and what is the structure of the RNA polymerase that binds to it? What part of the polymerase binds to the promoter? What is the difference between a strong and a weak promoter? Why does the closed complex open? What happens to the RNA polymerase when the open complex forms? What are the channels in the RNA polymerase? Why is each important? Why does the RNA polymerase repeatedly make a short RNA segment before continuing? During elongation, how does the RNA polymerase fix errors? Why does RNA polymerase terminate RNA synthesis? What are the two types of termination? How does each of these processes work? What are the elements that are commonly found in eukaryotic promoters, and where are they typically located? What are the regulatory elements that are found further away from the promoters? What is the process of initiation? When does each of the proteins bind, and what are they doing to help with the transcription initiation? What is interesting about the CTD of RNA polymerase II? Why is the tail important? What is the importance of TBP? Where does it bind DNA? What happens when it binds? What are TAFs? What are some of the functions of these factors? Where does TFIIB bind? What does this say about its structure? What does TFIIF do in initiation? What do TFIIE and TFIIH do in initiation? What are mediators? Where do they bind and what is their purpose? What happens at the switch from initiation to elongation? What is the role of P-TEFb? What is the role of TFIIS and ELL in elongation? How are histones handled during transcription? Which proteins are involved and what is the process? When and how does the processing of mRNA start? What is a CAP, and how is it added? What causes the capping machinery to fall off? How does poly-A addition occur? What are the steps in this process? How does termination of transcription occur? What are the two methods proposed in eukaryotes? What does the RNA polymerase I promoter look like? What factors are necessary for it to work? What does the RNA polymerase III promoter look like? How do factors help transcription for this set of genes? RNA splicing How many introns are in genes? What is the relative size of introns vs. exons? What is alternative splicing? How frequent is this process? How many proteins can be made for one gene? Why does the DSCAM gene in Drosophila make so many proteins? What are the necessary parts of an intron? What are the two reactions that need to occur during splicing? What is trans-splicing? Where does it usually occur? What are spliceosomes? What are U RNAs? What are snRNPs? What RNA interactions occur between U RNAs? What proteins interact with RNA or other proteins to help the splicing? What is the overall splicing pathway? What happens at each step and which proteins are involved? 2 What are the types of self-splicing? What is the mechanism of group I splicing? What are some common types of splicing errors? What is the splicing order of introns? How does the cell increase the chance of splicing near exons instead of other sites? What is the rare form of spliceosomes? How do they differ from the normal form? What is alternative splicing? What are examples of the types of alternative splicing that can occur? What are three ways that alternative splicing can be ensured? How is the Dscam gene in Drosophila spliced? How is alternative splicing regulated? What are ESE, ISE, ESS, and ISS? How can these affect splicing? How do SR proteins bind and activate splicing? How do silencers differ from enhancers from a structural viewpoint? How is the Double-sex (dsx) gene in Drosophila regulated? What is exon shuffling? What are the two models that try to explain why introns are present in eukaryotes and not in prokaryotes? What is RNA editing? What are the two types of editing? What are the processes that cause the editing? How is mRNA export regulated? How can this regulation reduce the chance of incorrectly made transcripts being exported? Old midterm 6) Explain both the Holiday and the Double-strand break models of recombination. What is different between the two models and what is the major evidence that supports the models? 1) Explain how Salmonella switches between different types of flagella. Include the important proteins and describe the switching process. 2) What is the difference between replicative and non-replicative transposition? Describe the basics of how each works and the difference between the two types. 3) Describe the general structure of RNA polymerase in E. coli (prokaryotic). Include the channels and other important parts of the structure. 4) Explain the process of assembling the pre-initiation complex for RNA polymerase II in eukaryotes. Include each transcription factor and what each is doing in this process. 5) What is the process of splicing? Include the important steps and proteins/structures in this process. 6) Explain how sex determination is regulated in Drosophila. Include all of the steps in the pathway that affect the Double-sex (dsx) gene. 3