* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Gene Expression
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
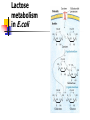
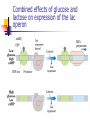
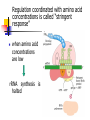
การควบคุมการแสดงออกของยีนในเซลล์ โปรคาริโอต (Control of Gene Expression in Prokaryotes) ผศ.ดร. ม ัญชุมาส เพราะสุนทร Gene Expression Expression of the genetic information that the DNA contains DNA RNA protein High cost of protein synthesis \Regulation of gene expression is essential to making optimal use of available energy Processes that affect the concentration of a protein the most efficient place for regulation is at the beginning of the pathway regulation at the level of transcription Principles of gene regulation constitutive gene expression genes for the enzymes of central metabolic pathways (housekeeping genes) regulated gene expression levels of some gene products rise and fall in response to molecular signals Induction repression inducible enzymes repressible enzymes RNA polymerase binds to DNA at promoters regulation of transcription how RNA polymerase interacts with a promoter RNA polymerase-promoter interaction influences the rate of transcription differences in promoter sequences regulatory proteins : interfering with the interaction between RNA polymerase and the promoter Transcription initiation is regulated by proteins that bind to or near promoters Types of proteins that regulate transcription initiation repressors : impede access of RNA polymerase to the promoter activators : enhance the RNA-promoter interaction (non-housekeeping genes) Most prokaryotic genes are regulated in units called “operon” gene cluster, promoter additional sequences that function together in regulation Lactose (lac) operon lac operon includes the genes for b-galactosidase (Z) permease (Y) transacetylase (A) Lactose metabolism in E.coli b-galactosidase is an inducible enzyme C-source Glucose/glycerol Lactose \ b-galactosidase b-galactosidase < 10 molecules/cell several thousands molecules/cell is an inducible enzyme lac operon in the repressed and induced states Inducers of the lac operon allolactose IPTG Inducible catabolic operons are globally regulated by CAP protein containing cAMP if both glucose and lactose are present “catabolite repression” prevents expression of the genes for catabolism of lactose, arabinose and other sugars in the presence of glucose the effect of glucose is mediated by cAMP CRP (cAMP receptor protein) or CAP (catabolite gene activator protein) When glucose is absent, CRP (CAP) binds to a site near the lac promoter and stimulating RNA transcription 50 fold Combined effects of glucose and lactose on expression of the lac operon Control of ribosomal protein synthesis is at the level of translation an increased cellular demand for protein synthesis increasing the number of ribosomes cells must coordinate the synthesis of ribosomal proteins (r-proteins) and rRNA the r-protein operons are regulated through a “translational feedback mechanism” also functions as a “translational repressor” at least one protein encoded by each ribosomal protein operon serves as a “translational repressor” binds to mRNA near the initiation site blocks translation of all the genes the rate of r-protein synthesis is kept in balance with rRNA availability rRNA synthesis responds to cellular growth rate availability of crucial nutrients, particularly amino acids Regulation coordinated with amino acid concentrations is called “stringent response” when amino acid concentrations are low rRNA synthesis is halted ppGpp is synthesized from ATP and GDP during amino acid starvation