* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download D. Eisenhower Polio Myelitis: A Virus which caused Nerve cell
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
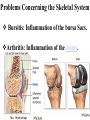
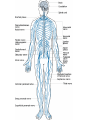
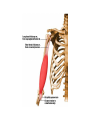
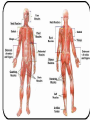
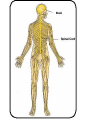
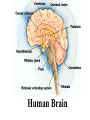
SKELETAL SYSTEM The Functions of Skeletal System Protect Act as Levers Serve as Attachments for muscles The Skeletal System Continued There are 206 bones in the human body. Examples of bones are: • Skull – Head • Jaw Bone – Mandible • Clavicle – Collar Bone • Scapula – Shoulder Blade • Humerus – Upper Arm • Radius/Ulna – Lower Arm •Carpals – Wrist Bones of the Skeletal System Continued: • Sternum – Breast Bone • Ribs (24?) • Vertebrae – Spinal Cord • Ilium – Hip Bone • Femur – Thigh Bone • Patella – Knee Cap • Tibia – Shin Bone • Fibula • Tarsals – Ankle/Foot I found the femur Facts Concerning the Skeletal System Inside the bone there is a hallow space filled with a sponge like substance know as Marrow where Red Blood Cells are produced. Bursa Sacs are located around the joints of the body and secrete Synovia Fluid which Lubricates the movements of the bones. Ligaments serve as connecting tissue holding bones together. Tendons hold muscles to bones. Cartilage Joints of the Human Body Ball and Socket Pivot Hinge Gliding Fused Problems Concerning the Skeletal System Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursa Sacs. Arthritis: Inflammation of the Joints. NERO-MUSCULAR SYSTEM The functions of muscles: •Provides force on the bones • Acts as a auxiliary pump for the Heart • Overcomes the forces of gravity The “All or None Law” of muscle physiology: If the stimulus reaches Threshold response (no matter how Strong or weak) then the whole muscle will contract and if it doesn’t then none of the muscle will contract. Examples of Muscles • Frontalis •Temporalis • Pectoralis Major • Deltoid • Biceps Brachi • Triceps • Rectus Abdominis • Rectus Femoris • Tibialis Anterior THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Heart Beat Respiration Digestion THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The Central Nervous System is made up of the brain and spinal cord. Sensory Nerves take messages to the brain. Motor Nerves take messages away from the brain. Association Nerve Cells are specialized nerve cells which intercept and direct a reflex motor response in order to protect the body. The Parts of the Brain Cerebrum contains centers for memory, intelligence, emotions, speech, hearing, and vision. Cerebellum contains centers that controls muscle movement. Mid-Brain and pons serve primarily as connecting stations for the brain. Medulla Oblongata contains centers for heart beat and respiration. Human Brain The Nerve Cell Function Axon takes message from one nerve to another. Dendrites receives the messages from an axon from another cell. Nota Bene: The axon and dendrite do not touch there is a gap between them. this gap is a bridged by a synapse facilitated by a chemical known as Acetyicholine which is active in the transmission of nerve impulses. The Nerve Cell DISORDERS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Julius Caesar EPILEPSY: Grand and Petite Mild believed to be caused by pressure on the brain. Dwight D. Eisenhower Stroke or Apoplexy: Oxygen is cut off to the brain. Brain damage may resul as well as loss of certain voluntary muscle functions. Woodrow Wilson Dr. Jonas Salk Franklin D. Roosevelt Polio Myelitis: A Virus which caused Nerve cell damage. Two doctors Invented vaccines to immunize people from Polio Dr. Salk via injection and Dr. Sabin developed an oral vaccine. Dr. Albert Sabin Multiple Sclerosis A disease marked by patches of hardened tissue in the brain or spinal cord resulting in partial or complete paralysis and muscular twitching. Parkinson’s Disease (PD) Michael J. Fox A degenerative disorder of the central nervous system that often impairs the suffers motor skills, speech, and functions i.e. muscle rigidity, tremor, slowing of and/or loss of physical movement. Janet W. Reno Lou Gehrig’s Disease Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) A progressive neuromuscular disease that weakens and destroys motor neurons that connect the brain with the skeletal muscles. Patients become paralyzed and often require ventilation. Loss of respiratory function is ultimately the cause of death.