* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cell Membrane and Homeostasis
Survey
Document related concepts
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
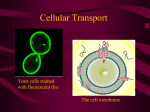
9/16/13 • Describe how temperature and pH affect enzymes using the graphs constructed Friday. • Summarize how you know enzymes have an optimal temperature and pH using graphs. 9/17/13 • Interpret the following graphs. Describe how temperature and pH effect enzyme activity. Analysis Questions • Digestive Tract Enzymes- function well in acidic environment • Alkaline- basic pH 8-14 • Intestine – 7-9 pH • Stomach – 1-4 pH 2nd – Enzyme Practice Question Groups 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Tony, Assyria, Quantavius Amber, Aaliyah F., Toretta Desiree, Maleka, Gary Deandre, Jeremy, Timonte Arquelius, D Moore, Keshawn Seth, Zykiyah, Amara Amberia, Khory, Toni Trayvon, Tanisha, Shambria Johnna, Briunna, Kierra 5th- Enzyme Practice Question Groups 1-Trenton, ShaQuavia, De'Juana, Isiah 2- Monkeize, Aaliyah, Darius 3- Jazmin, Esmeralda, LaKesha 4- Nah'ja, Antario, Nala 5- Michael, Ca’Darius, Michaela 6- Anterica, Walter, Roderick 7- Odyssey, Alexis, Tre 8- Damion, Javarus, Demarcus 9/18/13 • Testing Day- This is an opportunity for you to showcase what you have learned. Remember, use the following testing strategies to help you “Perform and Achieve”: – Underline key concepts – Circle distracters – Eliminate choices you KNOW are wrong Science Notebook • Complete pages 67 and 69` Reading Essentials • Begin Reading Chapter 7 Section 2- Plasma Membrane • Underline/highlight as you read 9/19/13 • Quick Write: CELLS Topic: Cell Membranes Standard and Essential Question • SB1. Students will analyze the nature of the relationships between structures and functions in living cells. • EQ: Analyze the structure of the cell membrane. How does the structure of the cell membrane enable cells to maintain homeostasis? Key Vocabulary 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Cells Prokaryote (n) prokaryotic (adj) Eukaryote (n) eukaryotic (adj) Homeostasis Maintain Cell/plasma membrane Phospholipid bilayer Passive transport Diffusion Osmosis Isotonic solution Hypertonic solution Hypotonic solution Facilitated diffusion 15. Active transport 16. Endocytosis 17. Exocytosis 18. Sodium (Na+) potassium (K+) pump 19. Transport protein 20. Cholesterol 21. Carbohydrate chains Create a Concept Map linking ALL vocabulary terms to demonstrate understanding of terms. Cell Facts • The average human being is composed of around 100 Trillion individual cells!!! • It would take as many as 50 cells to cover the area of a dot on the letter “i” • Cells are too small to be seen with the unaided eye • Before microscopes were invented, scientists knew very little about cells • p. 95, Fig. 6.2 Microscope Technology • Compound Light Microscopes – Has glass lenses that uses visible light to magnify images – Most commonly used microscopes (what we use) • Electron Microscopes – Transmission Electron Microscope • Passing electrons through a specimen on to a fluorescent screen – Scanning Electron Microscope • Passing electrons OVER a specimen to produce a 3-D image Discovery of Cells • 1665- English Scientist, Robert Hooke, discovered cells while looking at a thin slice of cork. • He described the cells as tiny boxes or a honeycomb • He thought that cells only existed in plants and fungi Anton van Leeuwenhoek • Father of microbiology • Dutch glass grinder who invented first microscope • 1673 - Used a handmade microscope to observe pond scum & discovered single-celled organisms • He called them “animalcules” (now known as protists) Development of the Cell Theory • 1838 - German Botanist, Matthias Schleiden, concluded that all plant parts are made of cells • 1839 - German physiologist and naturalist, Theodor Schwann, who was a close friend of Schleiden, stated that all animal tissues are composed of cells. Development of the Cell Theory • 1858- Rudolf Virchow, German physician/botanist/politician, after extensive study of cellular pathology, concluded that cells must arise from preexisting cells. • “All cells come from other cells” Omnis cellula e cellulaz • Therefore, it was known that cells are found in animals as well as plants The Cell Theory The 3 Basic Components of the Cell Theory were now complete: 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells. (Schleiden & Schwann)(1838-39) 2. The cell is the basic unit of life in all living things. (Schleiden & Schwann)(1838-39) 3. All cells are produced by the division of preexisting cells. (Virchow)(1858) Modern Cell Theory • Modern Cell Theory contains 4 statements, in addition to the original Cell Theory: 1. Cells contains hereditary information (DNA) which is passed on from cell to cell during cell division. 2. All cells are basically the same in chemical composition and metabolic activities. 3. All basic chemical & physiological functions are carried out inside the cells (movement, digestion, etc) 4. Cell activity depends on the activities of sub-cellular structures within the cell (organelles, nucleus, plasma membrane, etc) How has the Cell Theory been used? • The basic discovered truths about cells, listed in the Cell Theory, are the basis for things such as: – Disease/Health/Medica l Research and Cures (AIDS, Cancer, Vaccines, Stem Cell Research, etc.) The Cell Membrane and Homeostasis 1 - Create Format Essential Question: What is the rationale and research behind Focused Note-Taking? 2 - Organize Notes • • • • • • • • Listen and take notes in your own words. Paraphrase what you hear. Skip lines between ideas. Abbreviate. Use symbols. Write in phrases. Use bullets/lists. Recognize cues. 3 - Review & Revise Notes Review & Revise Notes continued… 4 - Note Key Ideas • Identify first “chunk” or “big idea” of the notes. • Write a question about the main idea of that “chunk” on LEFT. • Repeat until all “chunks” are identified with corresponding questions. Types of Cells • 2 types of cells 1. Prokaryotic –no nucleus 2. Eukaryotic – contains a nucleus Types of Cells : Similar Structures 1. 2. 3. 4. Cytoplasm Ribosomes Genetic information (DNA and RNA) Cell/ plasma membrane The Plasma Membrane Functions of the Cell Membrane • “Selective Permeability” • Controls what enters and leaves the cell Structure of the Cell Membrane • • • • • Mostly Made of Lipids “Phospholipid Bilayer” Polar, hydrophilic (water-loving) heads Nonpolar, hydrophobic (water-fearing) tails Proteins, cholesterols, & carbohydrate chains located throughout cell membrane • PLEASE see diagram p. 188!! “Phospholipid Bilayer” Functions: Proteins, Carbohydrates, & Lipids make the Cell Membrane • Proteins – Receptor Proteins • Sends messages to the inside of the cell – Transport Proteins • Move substances in and out of the cell • Carbohydrates – Cell identity ~ helps tell cells apart from one another • Cholesterol – Helps cell to maintain flexibility 9/20/13 Which of these describes the primary function of the cell membrane? A. They allow all materials to enter and exit the cell B. They allow certain materials to enter and exit the cell C. They do not allow molecules to enter or exit the cell D. they allow all materials to enter the cell, but not exit Fluid Mosaic Model • Cell membrane described as a fluid mosaic model. Fluid Mosaic Model:“Fluid” • Refers to the phospholipid bilayer. • Molecules are not bonded together, so are free to shift. • Must remain "fluid" for membranes to function. Fluid Mosaic Model:“Mosaic” • Proteins: float in a sea of phospholipids. • Proteins form a collage or mosaic pattern that shifts over time. Cellular Transport Cellular Transport • Two types of Cellular Transport 1. Passive Transport 2. Active Transport • Passive Transport – Transport across the cell membrane that DOES NOT require energy Active Transport Transport across the cell membrane that DOES require energy Passive Transport 1. Diffusion 2. Osmosis 3. Facilitated Diffusion Passive Transport: Diffusion • Diffusion – Movement of particles from an area of high concentration to low concentration until both sides are equal Passive Transport: Osmosis Diffusion of WATER Water moves in the direction of higher solute concentration in order to dilute it until both sides are equal Equilibrium Passive Transport: Osmosis:Tonicity • Isotonic Solution – Same concentration on both sides – Water moves in and out of cell at the same rate • Hypertonic Solution – Concentration of solute outside the cell is HIGHER than inside the cell – Water moves OUT of cell • Hypotonic Solution – Concentration of solute outside the cell is LOWER than inside the cell – Water moves INTO cell Cell in Isotonic Solution 10% NaCL 90% H2O ENVIRONMENT CELL 10% NaCL 90% H2O NO NET MOVEMENT What is the direction of water movement? equilibrium The cell is at _______________. copyright cmassengale 47 Cell in Hypotonic Solution 10% NaCL 90% H2O CELL 20% NaCL 80% H2O What is the direction of water movement? copyright cmassengale 48 Cell in Hypertonic Solution 15% NaCL 85% H2O ENVIRONMENT CELL 5% NaCL 95% H2O What is the direction of water movement? copyright cmassengale 49 A. B. C. 1. Hypertonic, Hypotonic, or Isotonic? 2. Which way will water move? 3. What happens to the cell? A. B. C. •Hypertonic •Water moves OUT •Shrink •Hypotonic •Water moves IN •Swell •Isotonic •Water moves in and out at same rate •No change 1. Hypertonic, Hypotonic, or Isotonic? 2. Which way will water move? 3. What happens to the cell? Factors that Effect Diffusion 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Concentration Temperature Pressure Particle size Mixing Osmosis Passive Transport: Facilitated Diffusion • Facilitated Diffusion – Requires the help of transport proteins when molecules are too large to diffuse through the membrane Active Transport 1. Endocytosis 2. Exocytosis 3. Sodium Potassium Pump Active Transport: Endocytosis Cell membrane surrounds a substance outside the cell, encloses it, and brings it INTO the cell Active Transport: Exocytosis Cell membrane surrounds a substance inside the cell, encloses it, and transports it OUTSIDE the cell http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=swf::535::535::/sites/dl/free/0072437316/120 068/bio02.swf::Endocytosis%20and%20Exocytosis Active Transport: Sodium Potassium Pump – Pumps 3 Sodiums (Na) outside the cell while pumping 2 Potassiums (K) into the cell – This pump helps energy (ATP) transformations that give the cell energy https://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter2/animation__how_the_sodium _potassium_pump_works.html Questions? 9/23/13 • Which structure is responsible for allowing materials into and out of an animal cell? A. Nucleus C. Mitochondrion B. cell wall D. cell membrane 9/24/13 • If an animal cell is placed in distilled water, it will swell and burst. The bursting of the cell is a result of which biological process? A. active transport B. enzyme activity C. osmosis D. respiration Friday’s Items • Completed Vocabulary – Concept map and summary – Frayer models (5th period ONLY) • Science notebook pages • Cornell Note Summaries 9/25/13 • When Streptococcus pneumoniae are exposed to an antibiotic, the bacteria try to pump the antibiotic out of their cells. Which of the following mechanisms is most likely used by the Streptococcus pneumoniae to pump the antibiotic out of their cells? A. Active transport B. Diffusion C. facilitated diffusion D. osmosis 9/26/13 • The diagram below shows changes in the concentrations of sodium and potassium ions inside and outside a nerve cell. These changes prepare the nerve cell to conduct an electrical impulse. Which of the following processes is directly responsible for these changes in the concentrations of sodium and potassium ions inside and outside the nerve cell? A. Active transport B. enzyme activity C.osmosis D. transcription 9/27/13 Use Cornell notes to answer the following questions. 1. Hypothesize how a cell would be affected if it lost the ability to be selectively permeable/ semipermeable? 2. Predict. What might happen to a cell if it no longer could produce cholesterol? Stages in the Construction of a Concept Map 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Brainstorming Organizing Layout Linking Revising Finalizing 1. Brainstorming • List all terms and concepts associated with the topic of interest 2. Organizing • Spread concepts on a blackboard so that they can be easily read • Create groups and subgroups of related items • Group items to recognize hierarchies (order) 3. Layout Stage • Arrange terms based on interrelationships and connections among groupings • Within sub-grouping, place closely related items nearer to each other 4. Linking phase • Use lines with arrows to connect the items. • Write a word or short phrases for each arrow to specify the relationship • Many arrows can originate or terminate on important concepts 5. Revising stage • Carefully examine the draft concept map • Rearrange concepts to emphasize organization and appearance • Remove or combine items to simplify • Consider adding color or different fonts 6. Finalizing map • Finalize the arrangement of items that conveys better understanding • Be creative by using colors, fonts and shapes Focus Terms-1st Set Cells eukaryote prokaryote homeostasis cell membrane phospholipid bilayer transport protein carbohydrate chains cholesterol Focus Terms- 2nd Set Passive transport Diffusion Osmosis Isotonic solution Hypertonic solution Hypotonic solution Facilitated diffusion Focus Terms- 3rd Set Active transport Endocytosis Exocytosis Sodium potassium pump Testing • Clear your desk • #2 pencil • Blank sheet of notebook paper Assignments • Science Glencoe Notebook (Due Friday, 9/27) – Pages 67, 69, 73-75 • Concept Map with summary (Due Friday, 9/27) • GIZMO: Osmosis- Prior Knowledge Questions (Due Thursday, 10/3) • Cell Membrane Worksheet (Due Thursday, 10/3) Assessment! • Cell Membrane and Transport Assessment Thursday. • 20 questions-cell membrane and transport • 5 questions- previously covered standards GIZMO: Account Set Up 1. www.explorelearning.com 2. Select enroll in a class 3. Enter class code: 1. 2nd period: 7NH3QCJJVP 2. 4th period: VDUPZ6EERL 3. 5th period: HJFWD24KC4 4. Register for a class 5. Username: first name lunch ID 6. Password: lunch ID 5th period- GIZMO groups • Coach Clark 1. Trenton, Odyssey 2. Michael, Esmeralda 3. Jazmin, Javarus 4. Nah’ja 5. Tre, De’juana 6. Isiah, Damian 7. Monkieze • Mrs. Gordon 1. Lakesha, Antario 2. Aaliyah, 3. Roderick, Darius, Roderick 4. Michaela 5. Anterica, Rutledge 6. Walter, Ca’Darius, Alexis GIZMO Discussion Questions 1. Which particles can pass through the semi permeable membrane shown in the Gizmo? Which particles cannot pass through? 2. What is the relationship between solute concentration and solvent concentration? 3. What happens when the solute concentration outside the cell is increased? Why? 4. What causes the cell to stop swelling or shrinking? 5. What do you think would happen if you placed a cell in pure water? 6. What do you think would happen if you placed a one-celled freshwater organism into the ocean? What would happen if you placed a one-celled marine organism into fresh water? 9/30/13 1. The plasma membrane consists of A. Two layers of lipids organized with the nonpolar tails forming the interior of the membrane B. Protein molecules arranged in two layers with polar areas forming the outside of the membrane C. Lipid molecules positioned between two carbohydrate layers D. Protein molecules with polar and nonpolar tails 10/1/13 1. What structure is characterized as being semi permeable and responsible for allowing nutrients and waste into and out of a cell? A. mitochondrion C. Cell wall B. nucleus D. cell membrane USAtestprep.com • Assignments need to be complete • No talking-ONLY working-preparing for Thursday’s Exam Vocabulary 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. Cell membrane/plasma membrane Homeostasis Passive transport Active transport Osmosis Hypertonic Hypotonic Isotonic Facilitated diffusion Diffusion Transport protein Cholesterol Phospholipid bilayer Hydrophobic hydrophilic 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. Endocytosis Exocytosis Sodium potassium pump Enzyme Lipid Concentration gradient Carbohydrate Nucleic acids Polar Semi permeable Selectively permeable Substrate Active site Products denature Differentiated Instruction • Students with Cornell notes- groups no larger than three- identify the main idea of your notes and create questions using DOK wheel at level 2 or higher • Students without cornell notes- compare and contrast passive and active transportcompare and contrast the three types of passive transport: diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion 10/2/13 1. Depending on its electric charge, shape, and chemical properties, a substance may or may not be allowed to pass through a cell membrane. This function of the cell membrane is important because it _______________. A. prevents cell division B. prevents destruction of the cell wall C. allows the cell to maintain homeostasis D. allows amino acids to move into and out of the cell 10/3/13 The diagram below illustrates how plant root cells take in mineral ions from the surrounding soil. Which of the following processes is illustrated? A. Active transport C. Osmosis B. diffusion D. passive filtration 10/4/13 • Please prepare assignments that are due Word Bank • • • • • • Part II- Questions #2-3 Increases Solute Solution A Solution B Isotonic • • • • • • • • Part III- Questions Isotonic Leave Osmosis Hypotonic Water Burst Cell wall 10/4/13 • Good Morning! • Please complete the “About Me” 1st period improvements • 117661 • 82057 Cellsalive.com • Click on interactive plant, animal and prokaryote models • Pick the organelles to get function and look at organelle