* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cell -- Membranes
Survey
Document related concepts
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Theories of general anaesthetic action wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Ethanol-induced non-lamellar phases in phospholipids wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
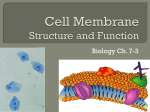
CELL MEMBRANES
and TRANSPORT
Regular Biology
Mr. Wilbrandt
1
Targets
I
will be able to…..
Identify
the parts of the cell or plasma
membrane
Compare
and contrast how the different
parts of the membrane work.
2
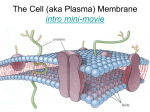
The Cell
3
Cell membrane
All living things are surrounded by a membrane.
A cell membrane is also known as plasma membrane.
Controls
exchange of materials such as nutrients and
waste between cells and their environment.
Has
other important functions for example to enable
cells to receive hormones.
To
understand the function of anything in biology, you
must study the structure first!
4
Cell Membranes from Opposing
Neurons (TEM x436,740).
Nerve cell
Cell membrane {
Gap between cells
}
cell membrane
7nm wide
Nerve cell
AS Biology. Foundation. Cell
membranes and Transport
5
Cell membranes are made of
PHOSPHOLIPIDs
HYDROPHILIC (+)
heads (water liking)
-Attracted to the
water
HYDROPHOBIC (-)
tails (water fearing)
-Not attracted to
the water
A Phospholipid
6
Phospholipids are important structural components of cell
membranes. Phospholipids are modified so that a phosphate group
(PO4-) replaces one of the three fatty acids normally found on a
lipid. The addition of this group makes a polar "head" and two
nonpolar "tails".
7
A phospholipid
HYDROPHILIC HEAD
At the other end of the phospholipid is a
phosphate group and several double
bonded oxygens. The atoms at this end
of the molecule are not shared equally.
This end of the molecule has a charge
and is attracted to water. It is POLAR
HYDROPHOBIC TAILS
The two long chains coming off of the
bottom of this molecule are made up of
carbon and hydrogen. Because both of
these elements share their electrons
evenly these chains have no charge. They
are NON POLAR. Molecules with no
charge are not attracted to water; as a
result water molecules tend to push
them out of the way as they are
attracted to each other. This causes
molecules with no charge not to dissolve
in water.
AS Biology. Foundation. Cell
membranes and Transport
3D model of a
Phospholipid
8
A Phospholipid Bilayer
Phospholipids can form:
BILAYERS
-2 layers of
phospholipids with
hydrophobic tails
protected inside by the
hydrophilic heads.
The PHOSPHOLIPID
BILAYER is the basic
structure of membranes.
9
10
Take Two…….
Take
a minute or two to discuss with
the person next to you what is meant by
polar head and non-polar tails.
What
do they look like?
11
Diagram representing the cell membrane
Remember the membrane is 7nm wide
12
Fluid mosaic model
Cell membranes also contain proteins within the phospholipid bilayer.
FLUID- because individual phospholipids and proteins can move around freely within
the layer, like it’s a liquid.
MOSAIC- because of the pattern produced by the scattered
protein molecules when the membrane is viewed from above.
13
Diagram of a cell membrane
14
Cell Membranes from Opposing
Neurons (TEM x436,740).
} Phospholipid Bilayer
7nm wide
AS Biology. Foundation. Cell
membranes and Transport
15
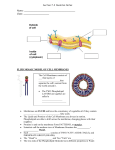
Features of the fluid mosaic model
Double layer – BILAYER of phospholipids which can move about by
………………………… in their own ……………………….
Phospholipid tails point inwards forming a ……. ………. ………………………… interior.
The phospholipid heads point outwards facing the aqueous (water containing)
medium surrounding the membrane.
Some phospholipids fatty acid tails are ……………………….. – straight so fit
together tightly. Some are ………………………… – bent so fit together …………………….
The more unsaturated tails there are the more ……………… the membrane
becomes. The lower the temp, the ……………….fluid.
Most protein molecules …………………. like icebergs in the layers, some are fixed
to ………………………. inside the cell and don’t float.
Some proteins are embedded in the outer layer, some in the inner layer and
some ………………… the two layers. Hydrophobic and Hyrdophilic parts of the
protein molecules sit next to the …………………………… and ………………………….. portions
of the ……………………………… of the membrane. This ensures the proteins stay in
the membrane.
The membrane is ……nm thick on average.
Some phospholipids have carbohydrates attached to them called………………………..
Some of the proteins have carbohydrates attached to them called–
……………………
The membrane also contains molecules of ………………………………..
16
Features of the fluid mosaic model
Double layer – BILAYER of phospholipids which can move about by DIFFUSION
in their own MONOLAYER
Phospholipid tails point inwards forming a NON-POLAR HYDROPHOBIC interior.
The phospholipid heads point outwards facing the aqueous (water containing)
medium surrounding the membrane.
Some phospholipids fatty acid tails are SATURATED – straight so fit together
tightly. Some are UNSATURATED – bent so fit together loosely. The more
unsaturated tails there are the more ‘fluid’ the membrane becomes. The lower
the temp, the less fluid.
Most protein molecules float like icebergs in the layers, some are fixed to
structures inside the cell and don’t float.
Some proteins are embedded in the outer layer, some in the inner layer and
some span the two layers. Hydrophobic and Hyrdophilic parts of the protein
molecules sit next to the Hydrophobic and Hydrophilic portions of the
phospholids of the membrane. This ensures the proteins stay in the membrane.
The membrane is 7nm thick on average.
Some phospholipids have carbohydrates attached to them – GLYCOLIPIDS
Some of the proteins have carbohydrates attached to them – GLYCOPROTEINS
The membrane also contains molecules of CHOLESTEROL
17
Movement of selected molecules
across the cell membrane
18
It’s Alive!!!
Moving
amoeba
AS Biology. Foundation. Cell
membranes and Transport
19
And so……
I
now am able to…..
Identify
the parts of the cell or plasma
membrane
Compare
and contrast how the different
parts of the membrane work.
20
The End
21