* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sensory Organs and Processes, Part II
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Patch clamp wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
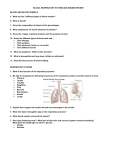
Taste Sensory systems 2 Sugar molecule G protein Sweet receptor Tongue Today s topics: • Sensory receptors – Chemoreceptors Taste pore • Taste and Smell Taste bud – Photoreceptors • Vision Sugar molecule SENSORY RECEPTOR CELL Sensory receptor cells IP3 (second messenger) • Nervous systems Sensory neuron – Afferent and efferent neurons – Sympathetic and parasympathetic – Organization of the brain (briefly) • Plant Senses ER Sodium channel Ca2+ (second messenger) Na+ 5 December 2016 Taste Humans have many bitter receptors. Each responds to just a few compounds. Smell Brain Action potentials Olfactory bulb Odorants Nasal cavity Bone Epithelial cell Odorant receptors e.g. TAS2R38 detects PTC Chemoreceptor Plasma membrane Cilia Odorants Mucus Each odor has a different receptor Fig. 50-17 Retina Retina Choroid Photoreceptors Neurons Vision Cone Rod Rod Light To brain INSIDE OF DISK Optic nerve cis isomer Light Light Enzymes Cell body CYTOSOL Ganglion cell Amacrine cell Optic nerve axons Synaptic terminal Horizontal cell Bipolar cell Rhodopsin Retinal Opsin trans isomer Retinal acts as a switch Pigmented epithelium 1 Fig. 50-19 Activation by light closes sodium channels and hyperpolarizes the cell EXTRACELLULAR FLUID Light Dark Responses Light Responses Rhodopsin inactive Rhodopsin active Na+ channels open Na+ channels closed Rod depolarized Rod hyperpolarized Glutamate released No glutamate released Bipolar cell either depolarized or hyperpolarized Bipolar cell either hyperpolarized or depolarized Active rhodopsin CYTOSOL cGMP Inactive rhodopsin GMP Sodium channel Na+ Membrane potential (mV) Dark 0 –40 Light Hyperpolarization –70 Na+ Time Compound eyes Other Senses? Trout have magnets in their noses. Others have a centralized nervous system (brain) Some animals just have neural nets Snakes sense infrared Bees see UV light Human Bees response of individual particles 2 Autonomous nervous system A very simple neural circuit Norepinephine Ach Organization of the brain Can plants smell? Butenolide receptors detect smoke Dodder uses odor to locate host plants Plants also use volatiles to warn of herbivores Can plants taste? Can plants hear? • Nutrient sensing by plant roots • No L H L 3 Can plants touch? • Tendrils coil after they touch a stem • Venus Fly Trap has trigger hairs. Can plants see? • Phototropism • Shade avoidance 4