* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
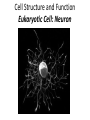
Download Cell Structure and Function Eukaryotic Cell: Neuron
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
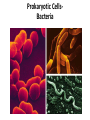
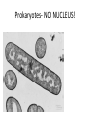
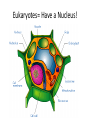
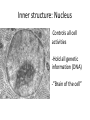
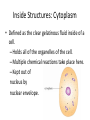
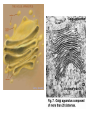
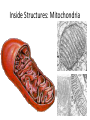
Cell Structure and Function Eukaryotic Cell: Neuron Cell Structure and Function Eukaryotic Cells- Red Blood Cells Prokaryotic CellsBacteria Prokaryotes- NO NUCLEUS! Eukaryotes= Have a Nucleus! Cell Structure and Function -All living organisms are made of cells. -A cell is a small, membrane enclosed structure filled with an aqueous solution where organelles and other subcellular structures are found. “subunit of life!” -Cells are of different size and shape -The cell’s size and shape can be related to its specific function. From Prokaryotes to Eukaryotes • It is thought that all organisms living now on Earth are derived from a single cell born 3,500 millions of years (my) ago – Primordial Cell -Simple organic molecules likely formed billions of years ago Unicellular vs. Multicellular Organisms • Why unicellular? • Why multicellular? Can we see Cells? • Some cells We are able to See without a Microscope Ex/ chicken egg, Egg yolk Structural Features of cellsOutside Covers All cells have a plasma or cell membrane, which contains the cell Plant cells and most bacteria have an outermost additional layer, the plant cell wall and the bacterial cell wall respectively Outside Cell Covers The plant cell wall is the outermost layer of plant cells • It provides extra protection to the plant Why do plants need these extra features? • Cell walls of adjacent plant cells are in close communication Inner Structures of the Cell The nucleus of eukaryotic cells is contained by the nuclear envelope. Inside the nucleus contains chromatin (DNA + DNA associated proteins) and a nucleolus Nucleolus: In the nucleus, makes ribosomes and nucleic acids found within the nucleus. Inner structure: Nucleus Controls all cell activities - -Hold all genetic information (DNA) -”Brain of the cell” Some cells lose their nucleus as they mature Ex/ RBC’s Inner Structures • Ribosomes: Make proteins! – Assembled by their instructions of DNA REVIEWWhat is a protein? Inside Structures: Cytoplasm • Defined as the clear gelatinous fluid inside of a cell. – Holds all of the organelles of the cell. – Multiple chemical reactions take place here. – Kept out of nucleus by nuclear envelope. Inside Structures: ER • Endoplasmic Reticulum: Proteins are made here A folded membrane found in the cytoplasm of a cell that provides a large surface area on which chemical reactions can easily take place. Inside Structures: ER Rough ER: Makes proteins Smooth: makes lipids, processing of sugars, and detoxification of drugs and Poisons -One of cell’s delivery systems Inside Structures: Golgi Apparatus • Golgi Apparatus: Closely stacked, flattened membrane sacs that receives newly made proteins and lipids from the ER -distributes them to the plasma membrane and other organelles throughout the cell. Inside Structures: Vacuole • Vacuole: Stores food, enzymes, and other materials needed by a cell. – A small percentage of vacuoles store waste products. – Vacuoles in plants cells are huge! • Usually only one. – Animal cells can have many small vacuoles. Inside Structures: Lysosomes • Lysosomes: Contain digestive enzymes. - They digest excess or worn out organelles, food particles, and engulfed viruses or bacteria – Their membrane prevents harmful enzymes from pouring into the cytoplasm of the cell. Inside Structures: Mitochondria • Mitochondria: Organelles in which food molecules are broken down (glucose) to produce energy. – Shaped like tiny sausages. – Have their own DNA/Ribosomes – Inner membrane forms long, narrow folds called cristae. Inside Structures: Mitochondria Inside Structures: Chloroplasts • Chloroplasts: Photosynthesis takes place here • Transforms light energy into chemicals to produce food • In plants only! Inside Structures: Chloroplasts • Chlorophyll: A green pigment that traps the energy from sunlight and gives plants their green color. • It is found in the thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast. • **What gives plants their green color** Inside Structures: Centriole • Helps in cell reproduction • Helps in cell division Structures for Support • Cytoskeleton: A network of thin, fibrous elements that provide support for organelles and helps the cell maintain its shape. – Microtubules: Thin, hollow cylinders of protein. – Microfilaments: Thin, solid protein fibers. – Both work together to provide support. Structures for Movement • Cillia: Hair-like projections” that beat together to create movement • Flagella: Long projections that move in a whiplike motion to produce movement. – The major method of locomotion in unicellular organisms. Cillia Flagella