* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nucleic Acids Powerpoint
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid tertiary structure wikipedia , lookup
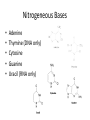
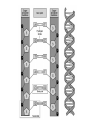
Nucleic Acids • Nucleic acids are large biomolecules (polymers) – essential for all known forms of life • Include DNA and RNA • Made from long strands of nucleotides (monomers) – A nucleotide contains a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base – The nitrogeneous bases are connected by the sugar and the phosphate group (rungs of the ladder) DNA vs. RNA • If the sugar molecule is Deoxyribose, the nucleic acid is DNA • If the sugar molecule is Ribose, the nucleic acid is RNA • RNA – mRNA, tRNA, rRNA Purines vs Pyrimidines Purines have a 2-Carbon nitrogen ring base Adenine Guanine Pyrimidines have a 1-carbon nitrogen ring base Thymine Cytosine Nitrogeneous Bases • • • • • Adenine Thymine (DNA only) Cytosine Guanine Uracil (RNA only) Chargaff’s Rule • Chargaff's rules states that DNA from any cell of all organisms should have a 1:1 ratio (base Pair Rule) of pyrimidine and purine bases and, more specifically, that the amount of guanine is equal to cytosine and the amount of adenine is equal to thymine. Base Pairing • The rules of base pairing (or nucleotide pairing) are: A with T: the purine adenine (A) always pairs with the pyrimidine thymine (T) • C with G: the pyrimidine cytosine (C) always pairs with the purine guanine (G) • The bases are paired with hydrogen bonds – 2 between A and T and 3 between C and G