* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Cycle part 2 - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Microtubule wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Kinetochore wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
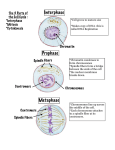
AP Biology The Cell Cycle Part 2 Centrioles Interphase Before and after the S phase Interphase cell (Look at the chromatin in the blue nucleus and the yellow cytoskeleton.) Start of Mitosis Cell in Prophase Mitosis “Division of the nucleus” Cell in Metaphase Cell in Anaphase Cell in Telophase and starting Cytokinesis One cell becoming two Motor Protein and the Spindle Fibers Chromosome movement Microtubule Motor protein Chromosome Kinetochore Tubulin subunits Animal vs. Plant LE 12-10 Nucleus Nucleolus Chromatin condensing Prophase. The chromatin is condensing. The nucleolus is beginning to disappear. Although not yet visible in the micrograph, the mitotic spindle is starting to form. Chromosomes Prometaphase. We now see discrete chromosomes; each consists of two identical sister chromatids. Later in prometaphase, the nuclear envelope will fragment. Cell plate Metaphase. The spindle is complete, and the chromosomes, attached to microtubules at their kinetochores, are all at the metaphase plate. Anaphase. The chromatids of each chromosome have separated, and the daughter chromosomes are moving to the ends of the cell as their kinetochore microtubules shorten. 10 µm Telophase. Daughter nuclei are forming. Meanwhile, cytokinesis has started: The cell plate, which will divide the cytoplasm in two, is growing toward the perimeter of the parent cell. Microscopic view of Mitosis in Onion root tips. Can you identify the stages? Checkpoints (Is all going according to plan?) • Question: All organisms must be able to reproduce to keep the species existent. Prokaryotes undergo Binary Fission and Eukaryotic cells undergo Mitosis. In no more than four sentences, explain one similarity and one difference between the two processes. In addition, explain the evolution link between the two processes. (5 Points) • • Scoring Rubric: 1pt. Discussion of one similiarity – Cytokinesis, DNA synthesis (S), or Maturion (G1) • 1pt. Discussion of one difference – G2 or Mitosis • 1pt. Discussion of Binary fission being first and evolving into Mitosis as DNA and organisms became more complex over time. • 1pt. Correct use of scientific terms. • 1pt. Answer has no more than three sentences. (Following Directions.)