* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Gene Regulation
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid tertiary structure wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
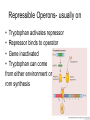
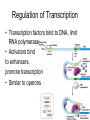
Gene Regulation Bacteria respond to environment • Must produce or absorb essential molecules • Turn on genes when environment is lacking target molecule • Turn off genes to save resources when target molecule is in environment DNARNA Protein Operons • Operator- switches on a group of adjacent genes • Repressor- binds to operator and prevents transcription • Repressor is reusable, can attach and detach from operator Repressible Operons- usually on • Tryptophan activates repressor • Repressor binds to operator • Gene inactivated • Tryptophan can come from either environment or rom synthesis Inducible operon- usually off • Lactose inactivates repressor • Repressor drops off DNA • Enzymes are transcribed • Once lactose is gone repressor binds again Metabolic pathways • Repressible enzymes anabolic pathways – Build up larger molecules – Once end product is present pathway turns off • Inducible enzymes catabolic pathways – Break down larger molecules – Turn on in the presence of starting product Eukaryotic, multicellular regulation • Regulate production of proteins at any point during transcription/translation Differentiation • Stem cells can turn into any type of cell • Zygote = undifferentiated – All genes are potentially active • Once a cell differentiates genes are turned off permanently • Regulation of genes can occur anywhere between chromosome and protein function Regulation of Chromosome Structure • Heterochromatin- condensed, not expressed • Euchromatin- uncondensed, expressed • Histone modification – Acetylation=prevents histones from binding to each other – Creates looser structure DNA modification • DNA Methylation – Addition of methyl groups deactivates DNA – Blocks RNA polymerase • Epigenetic Inheritance – Inheritance of DNA and chromosome modifications – Bees (worker vs. queen) – Potato famine diabetes Transgenerational epigenetic observations See main article Transgenerational epigenetics In the Överkalix study, Marcus Pembrey and colleagues observed that the paternal (but not maternal) grandsons[56] of Swedish men who were exposed during preadolescence to famine in the 19th century were less likely to die of cardiovascular disease. If food was plentiful, then diabetes mortality in the grandchildren increased, suggesting that this was a transgenerational epigenetic inheritance.[57] The opposite effect was observed for females—the paternal (but not maternal) granddaughters of women who experienced famine while in the womb (and therefore while their eggs were being formed) lived shorter lives on average.[58] Regulation of Transcription • Transcription factors bind to DNA, limit RNA polymerase • Activators bind to enhancers, promote transcription • Similar to operons RNA regulation • RNA processing – Alternative splicing • mRNA degradation – Micro RNA (miRNA) blocks or degrades RNA – Small interferring RNA (siRNA) • Regulatory proteins block attachment of ribosome at 5` end Protein Regulation • Polypeptides must be processed before becoming active proteins • Lifespan of protein – Regulatory proteins are short lived – Tagged with ubiquitin – Proteosomes degrade tagged proteins Non-coding DNA • 1.5% =exons • 24%=introns • 74.5% = repetitive DNA, non-coding regions, transposable elements Transposable elements • • • • Segments of DNA that move around Repeat many times Function unknown Alu repeats – ~300 nucleotides long – Unique to humans and primates – Used for DNA fingerprinting Evolution of the genome • Earliest life forms had very few genes – Minimum necessary for survival • Modern genomes are larger, more complex – Non coding regions – Regulatory genes – Operons