* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cell Membrane
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
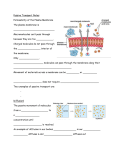
The Cell Membrane Aka: plasma membrane What is the cell membrane made of? 2 layers of phospholipids Carbohydrate & proteins embedded in the lipids. The phospholipids Fluid Mosaic Model Questions… • What is the MAJOR component (part) that makes up the cell membrane? • What is the name of the model we use to show the structure of the cell membrane? 2 types of proteins 1) Integral – usually go completely through the membrane, act as channels. 2) Peripheral – usually on the surface, act for communication or attachment sites. Can everything pass through the cell membrane? NOPE! The cell membrane is selectively permeable, only certain things are let through. Question… • Which type of protein in a cell membrane is used to help the cell communicate with other cells with neurotransmitters or hormones? 2 main forms of transport across the cell 1) Active – requires energy, usually moves substance against a gradient. 2) Passive – does not need energy, usually moves substances down the gradient. What are the different types of active transport? 1) Pumps - protein channels assist in the movement of substances. EX: Na-K pump 2) Exocytosis Moves large molecules or amounts OUT of the cell 3) Endocytosis Moves large molecules or amounts into the cell. Passive transport With passive transport, the goal is EQUILIBRIUM. Once equilibrium is reached there is no NET MOVEMENT. Types of passive transport 1) Diffusion – movement of a substance through a semi-permeable membrane from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. diffusion 2) Osmosis Movement of water down a concentration gradient. Water moves TOWARDS hypertonic areas Hypertonic A cell put in a hypertonic solution will shrink!!! Hypotonic A cell put in a hypotonic solution will swell and may burst! Isotonic When the concentration gradient across the membrane is the same, there is no NET movement. The cell will stay the same. Question… • If a cell is put in a glass of REALLY sugary water, will the cell shrink or swell? 3) Facilitated diffusion Carrier proteins help move substances across the membrane. Questions… • Are pumps active or passive? • Is diffusion active or passive? • Is osmosis active or passive? cell transport