* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Division
Survey
Document related concepts
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
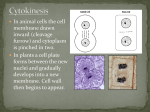
Chapter 10 Cell Division Prokaryotic Division Chromosomes (colored bodies) Prokaryotes have a single, circular chromosome • Prokaryotics Cell Division Prokaryotes (bacteria) reproduce through cell division Binary fission Circular chromosome (DNA) is replicated Replicated chromosomes are attached to the cell membrane at nearby sites As membrane expands, the copies separate New cell wall forms between copies, cell splits What about eukaryotic division? Mitosis Eukaryotes use cell division to create new cells MITOSIS: division of the nucleus Growth, Maintenance and Repair Asexual cell division Reproduction MEIOSIS: a special, two-stage type of mitosis that results in daughter cells with half as many chromosomes as the parent cells Humans 46 chromosomes Diploid state (2n = 46) 2 sets of 23 chromosomes (diploid) n = number of chromosomes in a set Fundamental number, haploid number In humans 23 n = contribution from each parent #23 = 1 sex chromosome, #122 autosomes Chromosomes Maternal Paternal Sex: X or X X or Y Autosomes #: 1 1 2 2 ä ä 22 22 (homologous pairs) The Cell Cycle The Cell Cycle shows the stages of life of a cell Cellular Division Cell division is how a cell makes a copy itself A cell spends most of its life in interphase 1st stage = G1, a growth phase; the number of organelles and the amount of cytoplasm double 2nd stage = S phase; DNA replicates (the chromatins turn into chromosomes) chromatins – loose uncoiled strands of DNA chromosomes – DNA wrapped around proteins How does DNA replicate? DNA Replication 3rd stage = G2, another growth phase; the cell will continue to grow The Cell Cycle Cellular Division After interphase, the cell goes through mitosis Mitosis is the next 4 phases of cellular division Mitosis occurs in all eukaryotic cells Only in your somatic cells Eukaryotic cells are cells that have a nuclei and membrane bound organelle Somatic cells are all body cells except for egg cells and sperm cells Mitosis Overview Phases of Mitosis First Phase – Prophase What happens during prophase? 1. Chromosomes condensed - become thicker 2. The nucleolus and nuclear membrane break down and disappear 3. Centrioles move to opposite sides of the cell 4. Spindle Fibers appear and radiate from the centrioles Spindle fibers are protein tubes What does prophase look like? Phases of Mitosis Second Phase – Metaphase What happens during metaphase? 1. Chromosomes move to the middle of the cell 2. Spindle fibers are attached to the chromosomes controlling their movement What does metaphase look like? Phases of Mitosis Third Phase – Anaphase What happens during anaphase? 1. The centromere breaks down The centomere holds the chromosomes together 2. The spindle fibers pull apart the chromosome Separating the sister chromatids What does metaphase look like? Phases of Mitosis Fourth Phase – Telophase What happens in telophase? 1. Nuclear membrane forms around chromatids This Forms a nucleus with a nucleolus 2. Chromatids turn into chromatins 3. The cell membrane starts to pinch inward to separate into 2 new cells 4. Centrioles and spindle fibers disappear What does telophase look like? Phases of Mitosis Cytokinesis is the last stage of cell division During cytokinesis the 2 cells actual split apart from each other In a plant cells, a cell plate grows between to the two new cell The cell plate develops into the cell wall What does cytokinesis look like?























![MITOSIS WORKSHEET - New Page 1 [bs079.k12.sd.us]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014668413_1-30813973b0cb9de17ced950a5cb16263-150x150.png)