* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Processes - cloudfront.net
Survey
Document related concepts
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
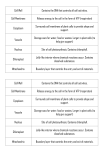
EOC REVIEW Cell Processes Day 3 Cell Theory 1. All cells come from pre existing cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function 3. All living things are made of cells Cell Organization Cell Tissue Organ Organ System Individual organism Cell to Cell Communication • Chemical Signals (hormones) can be sent from one cell to another • Receptor proteins on the plasma membrane receive the signal Prokaryotes Simple, no membrane bound organelles such as mitochondria Bacteria only Includes: chromosome, ribosome, and plasma Review membrane Questions Both Ribosomes DNA Cytoplasm Cell membrane Eukaryotes • Complex, contains membrane bound organelles • Have a true nucleus containing chromosomes • Includes: protists, fungi, plants and animals 1. What are the levels of cell organization? CellTissueOrganOrgan SystemIndividual Organism 2. What do eukaryotes have that prokaryotes don’t have? Eukaryotes contain a nucleus and membrane bound organelles Organelles- compartment for carrying out a specific job/reaction • Chloroplast: Photosynthesis, plant cell only • Mitochondria: “powerhouse” of the cell, produces energy in ATP form, cellular respiration • Ribosomes: protein synthesis, in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. A protein is a polymer made of a series of amino acid monomers. Examples of protein are some hormones and enzymes • Lysosome- digest waste/ food material • Vacuoles: storage of materials. Plants have one large vacuole • Nucleus: control center, contains DNA/chromosomes • Nucleolus: makes ribosomes • Endoplasmic Reticulum• Rough – transports protein • Smooth – synthesizes lipids and membranes EOC REVIEW Animal Cell Plant Cell No cell Wall • Cell Wall Cell Membrane • Cell Membrane No Chloroplast One or more small vacuoles • Contain Chloroplast • Large Vacuole • No centrioles Review Questions 1. Name one organelle a plant cell has that an animal cell doesn’t. Chloroplast, cell wall, large vacuole 2. Name one organelle an animal cell has that a plant cell doesn’t. Centrioles 3. Name one organelle an animal cell and plant cell have in common. Cell membrane, mitochondria, ER, golgi apparatus… Plasma Membrane AKA Cell Membrane • Surrounds the cell • Regulates what enters and leaves the cell • Helps maintain homeostasis • Made of phospholipids with embedded proteins Osmosis & Diffusion- Passive Transport • • Diffusion: solutes move from high to low concentration Osmosis: diffusion of water from high to low water concentrations through a semi permeable membrane Hypotonic – water enters cell Hypertonic – water exits cell Isotonic – equal movement of water in and out of cell • • • • Does not require energy: Passive Transport Ex: cell is salt water shrivels & cell in fresh water swells Ex: Turgor pressure in plants- wilted plants do not have enough pressure Ex: regulating the amount of water lost during transpiration due to opening and closing in stoma and guard cell. EOC REVIEW Facilitated Diffusion • Movement of a substance down its concentration through a transport protein channel Review Questions 1. What is passive transport? Movement of molecules from a high to low concentration: Does not require energy. 2. What are the examples of passive transport? Diffusion and Osmosis 3. What does semi permeable mean? Some (semi) particles can enter/leave and others cannot Active Transport • Particles move against the concentration gradient from low to high concentration, which REQUIRES ENERGY (ATP) Endocytosis: process by which cells take in material o Phagocytosis: the process of a cell engulfing solid particles o Pinocytosis: cells engulf liquid particles Exocytosis Energy process which a cell releases contents out of the cell membrane Review Questions: Fill in this chart. Also give the letter or number of the part as seen in the diagrams below. Cell Part and Letter Structure Description Function Nucleus Contains cells heredity information Control center of the cell and controls growth & reproduction. Plasma Membrane Also known as cell membrane. Controls the movement of Protects the interior of the cell. substances in and out of the cell. Cell wall Made up of cellulose. A tough outside layer surrounding a plant cell. Mitochondria Provides the cell with energy. “Powerhouse” of the cell. Vacuoles Chloroplasts Plants have one large vacuole. Animals have one or more small vacuoles. Only in plant cells. Ribosomes Carry out photosynthesis. Synthesizes (makes) proteins. Protein production. Comparison of active and passive transport PASSIVE TRANPORT Requires energy? Does NOT require energy Low to high concentration or high to low concentration? Examples Storage of materials. ACTIVE TRANSPORT Requires Energy (ATP) High to Low Low to High Diffusion/Osmosis Endocytosis & Exocytosis EOC REVIEW 1. Which cell is the plant cell (left or right)? LEFT 2. Which structures are found only in the plant cell? Cell wall, chloroplast, large vacuole 3. Which structures are found only in the animal cell? Centrioles