* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1 - mrnicholsscience
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
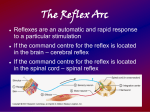
1. What are the basic elements of a reflex arc? 2. What is the minimum number of neurons in a reflex arc? Where is the extra neuron in the typical reflex arc? 7. Where are the primary sensory area and the primary motor areas of the brain? 8. Why does the primary sensory area have a large area for the face, but a small area for the thigh, even though the thigh is much bigger? 3. What is the main pathway between the brain and the PNS? 9. Name the layers of the meninges from outside to inside. 4. What does CSF flow through between the third and fourth ventricles? Where does CSF go when it leaves the brain? 10. What is the main function of the meninges? 5. What division of the nervous system produces movements in skeletal muscle? 11. Name two major folds of the meninges. Where is each located? 6. What does the central sulcus separate? 12. What part of the brain controls emotions? Blood pressure and swallowing? 13. Name and locate the lobes of the brain. 20. What is the difference between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems? 14. What are the three major structures of the diencephalon? 15. What are the important parts of the midbrain? 16. What are the four spinal nerve plexuses? 17. Name four major nerves of the arm and four major nerves of the leg. 18. What spinal nerve plexuses contribute to the leg? 19. What is the largest peripheral nerve in the body? 21. What is the difference between the autonomic and somatic nervous systems? 22. Match: (craniosacral/thoracol umbar) with (sympathetic/parasym pathetic) 23. Match: (motor/sensory) with (efferent/afferent) and (to CNS/from CNS) 24. Where are the nerve cell bodies of sensory nerves located? 25. Describe the knee tendon reflex and the withdrawal (jerk) reflex. 26. What is the function of the olfactory area, gustatory area, and Broca’s area? 27. What type of neurons are found in gray matter? 28. What nerve innervates the heart? 29. What separates: the cerebrum from the cerebellum? The two cerebral hemispheres? The frontal and parietal lobes? The temporal and frontal lobes? 31. What are the cervical and lumbar enlargements? 32. What is the cauda equina? 33. What do the thoracic spinal nerves do? 34. Name two major folds in the meninges, and locate them. 35. What is a gyrus, a sulcus, a fissure, and a lobe? 36. What does the cerebellum do? The thalamus? 30. What is a spinal tap? 37. ? 38. Name and give the function of six types of neuroglial cells 44. Describe the structure and function of the corpus callosum 39. What makes white matter white? 45. What is a ventricle? 40. How is an action potential conducted down an axon 41. Describe the location of gray and white matter in the brain and spinal cord. 42. Name the twelve cranial nerves. What does each cranial nerve do? 43. Describe the two roots and the rami of a typical spinal nerve. 46. Describe the structure and function of a synapse.