* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 8 Questions
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Theories of general anaesthetic action wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
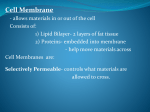
Chapter 8 Questions Vocabulary: phospholipid, lipid bilayer, equilibrium, concentration gradient, diffusion, carrier protein, osmosis, sodium-potassium pump, signal, receptor protein, second messenger, isotonic, hypotonic, hypertonic, active transport, passive transport, facilitated diffusion 1. Relate the functions of the cell membrane to homeostasis. 2. Describe the types of substanes that can pass through the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane. 3. Outline four functions of proteins within the cell membrane. 4. What would happen if the cell membrane were fully permeable to all substances in the cell’s environment? 5. Why can’t ions pass through the cell membrane? 6. Why does oxygen diffuse into the cell? 7. Compare the functions of channel proteins and carrier proteins in facilitated diffusion. 8. Explain why the presence of dissolved particles on one side of a membrane results in diffusion of water across the membrane. 9. List two ways that a cell can move a substance against its concentration gradient. 10. Based on what you have learned about homeostasis and osmosis, why should humans avoid drinking sea water? 11. Identify one function of signal molecules in a multicellular organism. 12. Describe the relationship between receptor proteins and signal molecules. 13. List three ways that a receptor protein may respond when a signal molecule binds to it. 14. Why do you think there are many forms of communication between body cells? 15. Why do you think specificity between a receptor protein and a signal molecule is important? 16. Distinguish between diffusion and osmosis. 17. Explain why the cell needs a selectively permeable membrane. 18. Describe the structure of the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane. 19. Contrast the action of carrier proteins in facilitated diffusion and active transport. Some Chapter 7 Review: 20. What is the limiting factor which determine how big a cell can become? 21. Fill in the following table: Side Length Surface Area to Volume Ratio Surface Area Volume SA/V Ratio 1mm 2mm 4mm 22. What does the prefix ‘cyto’ mean? What three words in this chapter have this prefix in them? 23. Use the following three words in the same sentence: prokaryote, eukaryote, nucleus. 24. Describe two observations of early scientists that support cell theory. 25. Describe how the structure of membranes in chloroplasts and mitochondria contributes to the function of these organelles.