* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Notes Chapter 10 Lesson 1 The Basics of a Cell
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
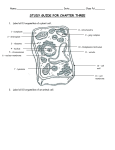
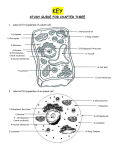
Notes Chapter 10 Lesson 1 The Basics of a Cell Cell- basic unit of structure and function in all organisms Organism Organization Cell Single Celled Organism- Living things that are made up of only ONE Cell Multi-celled Organism- Describes organisms that are composed of different kinds of specialized cells Cell Organism Tissue Organs Red Blood Cells Blood System (transport system) Organ Systems Heart Human Circulatory Cell Single Celled Organism— Atoms Organelles Cell Multi- celled Organism— Cell Organism Tissue Organs Organ Systems Organelles - Cell parts devoted to specific functions – Organs of a cell Difference of a Plant and Animal Cells Plant cells have two more parts than the animal cells have---Cell wall and Chlorophyll Organelles Nucleus - Brain of the cell - DNA Genetic Material - RNA Nuclear Membrane - Outer cover of the nucleus - Protects and allows material to enter and exit the Nucleus Cellular Membrane - Outer cover of an animal cell - Inside of the cell wall on a plant cell - Allows material to enter and exit a cell - Protects - Shapes Vacuoles - Storage - Food, water, minerals, and waste Ribosomes - Factories - Manufacture proteins - Some float - Some are attached to ER (Endoplasmic Reticulum) Endoplasmic Reticulum - Connects nuclear membrane with cell parts - Moves material - Highway - Long- winding membrane Golgi Body - Packing plant - Packages proteins made by the ribosomes and then ship Them out to where they are needed Mitochondria - Power house - Produces energy