* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download STUDY GUIDE FOR CHAPTER THREE
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
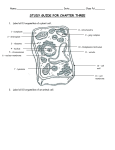
KEY STUDY GUIDE FOR CHAPTER THREE 1. Label all 13 organelles of a plant cell. 8-Mitochondrion 1-Cytoplasm 2–Chloroplast 9–Golgi Complex 3-Ribosome 4-Nucleus 5-Chromosomes (inside nucleolus) 10–Endoplasmic Reticulum 11-Vacuole 6-Nuclear Membrane 12–Cell Wall 7-Lysosome 13–Cell membrane 2. Label all 10 organelles of an animal cell. 6-Mitochondrion 7-Ribosome 1-Endoplasmic Reticulum 2-Nucleus 3 – Chromosomes (inside nucleolus) 4-Nuclear Membrane 5-Lysosome 8-Cell Membrane 9-Cytoplasm 10-Golgi Complex 3. Identify the three organelles in a plant cell which an animal cell does not have. 1. Large central vacuole 2. Cell Wall 3. Chloroplast 4. Identify the organelle in an animal cell which a plant cell does not have. 1. Lysosome 5. Who was the first person to discover cells? What tool did he build to see them? Robert Hooke – discovered cork cells by looking through his microscope 6. Who are the three scientists (last name only) that developed the cell theory? 1. Schleiden 2. Schwann 3. Virchow 7. What are the three parts of the cell theory? 1. All organisms are made of one or more cells 2. The cell is the basic unit of all living things 3. All cells come from existing cells 8. Explain the difference between a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell. -Prokaryotic Cells: an organism that consists of a single cell that does not have a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles -Eukaryotic Cells: an organism made up of cells that have a nucleus enclosed by a membrane; most are multicellular 9. List of levels of organization of living things beginning with the organelle (lowest level) to organism (highest level). Define each term. 1. Organelle Definition: Tiny organs inside cells that perform specific functions 1. Cell Definition: The smallest functional and structural unit of all living organisms 2. Tissue Definition: A group of similar cells that perform a common function 3. Organ Definition: A collection of tissues that carry out a specialized function of the body 4. Organ System Definition: A group of organs that work together to perform body functions 5. Organism Definition: A living thing; anything that can carry out life processes independently 10. What are the 3 benefits of being multicellular? Why are these things beneficial? 1. Larger size WHY? Multicellular organisms are prey for fewer predators and can eat a wider variety of prey 2. Longer life WHY? The life span of a multicellular organism is not limited to the life span of any single cell 3. Specialization WHY? Makes the organism more efficient 11. What is the difference between smooth endoplasmic reticulum and rough endoplasmic reticulum? Smooth ER: has no ribosomes attached. Its purpose is to make lipids and breaking down toxins that could damage the cell. Rough ER: is the location of the ribosomes. This is where proteins are made. It is usually near the nucleus. 12. Pick three terms/scientists that are the hardest for you to remember, and write ways to help you remember them on the test. You can use analogies, pictures, or words. Word #1:______________________________ Way to remember the word: Word #2:______________________________ Way to remember the word: Word #3:______________________________ 13. Way to remember the word: REVIEW: State the six characteristics of living things (from your in-class poster). 1. Living things are made up of one or more cells 2. Living things sense and respond to change 3. Living things reproduce 4. Living things have DNA 5. Living things need and use energy 6. Living things grow and develop 14. REVIEW: State the 4 basic needs of all living things. 1. water 2. food 3. air 4. shelter 15. REVIEW: List the five building blocks of living thing and one function of each. 1. Building Block: Protein Function: Help cells do their job, protect cells, build and repair body structures, speed up chemical reactions 2. Building Block: Lipids Function: Store fat; source of energy; form part of the cell membrane 3. Building Block: ATP Function: Major source of energy in a cell 4. Building Block: Nucleic Acid Function: Blueprint of life – instructs the cell how to make proteins 5. Building Block: Carbohydrates Function: Source of energy; store energy YOU ALSO NEED TO STUDY ALL VOCABULARY WORDS FROM THIS UNIT.