* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nucleus - mr-youssef-mci
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Microtubule wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
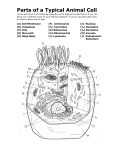
Nucleus where genetic information is stored determines the structural characteristics of cell and how it functions. (a) Chromatin – uncoiled DNA (b) Nucleolis – produces RNA used to make proteins Ribosomes Has a large and small subunit made up of ribosomal RNA and protein Free ribosomes – in cytoplasm, helps make proteins that will be used in cell Bound ribosomes – bound to rough ER, helps make proteins that will be sent to the outside of the cell or to the plasma membrane Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (Rough ER) Takes proteins (which were made with the help of bound ribosomes) and modifies and processes them so they can be sent to the Golgi Apparatus. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (Smooth ER) Makes macromolecules such as lipids (e.g. phospholipids), produces hormones and sends materials to the plasma membrane or Golgi Apparatus Golgi Apparatus Completes the processing of macromolecules (e.g. lipids and proteins) to make them fully functional Sorts and packages macromolecules, so they are ready for transport. Transport Vesicles Membrane bound organelles that carry material to different areas within the cell (e.g. carries proteins from rough ER to Golgi, and from Golgi to cell membrane) Mitochondria Site of respiration (where energy in macromolecules is transformed into a useable form) (a) Cristae - folds of inner mitochondrial membrane – increases the surface area for enzymes to make ATP Chloroplast (plant cell only) Location of photosynthesis Contains chlorophyll (green pigment) that absorbs sunlight and creates glucose Lysosomes Contain digestive enzymes that break down macromolecules or other large structures (e.g. damaged organelles) Formed from the Endoplasmic Reticulum Peroxisomes Breaks down large fatty acid chains and detoxifies alcohol (found in liver, kidney, brain) Formed in the cytoplasm Peroxisomes are membrane-bound packets of oxidative enzymes. In plant cells, peroxisomes play a variety of roles including converting fatty acids to sugar and assisting chloroplasts in photorespiration. In animal cells, peroxisomes protect the cell from its own production of toxic hydrogen peroxide. As an example, white blood cells produce hydrogen peroxide to kill bacteria. The oxidative enzymes in peroxisomes break down the hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen. Cytoskeleton (Actin, Intermediate Filaments, Microtubules) Organizes location of organelles within cytoplasm Gives shape to the cell Allows movement of organelles throughout cell Centrosome The centrosome, or MICROTUBULE ORGANIZING CENTER (MTOC), is an area in the cell where microtubules are produced. Centrosomes coordinates activities of spindle fibers when cell divides Plant and animal cell centrosomes play similar roles in cell division, and both include collections of microtubules, but the plant cell centrosome is simpler and does not have centrioles. Involved in the formation of cilia and flagella Cilia Short, cylindrical projections from cell that produce wave-like motions that move the cell in its environment Moves particles out of the lungs Flagella Long projections produce whip like motion to move cell. Centriole (animal cells only): Each centriole is a ring of nine groups of fused microtubules. There are three microtubules in each group. Microtubules (and centrioles) are part of the cytoskeleton. In the complete animal cell centrosome, the two centrioles are arranged such that one is perpendicular to the other. During animal cell division, the centrioles replicate (make new copies) and the centrosome divides. The result is two centrosomes, each with its own pair of centrioles. The two centrosomes move to opposite ends of the nucleus, and from each centrosome, microtubules grow into a "spindle" which is responsible for separating replicated chromosomes into the two daughter cells. Cell Wall (plant cell only) Contains cellulose fibers Adds strength and rigidity to the cell Prevents cell from bursting in hypotonic environment Vacuole: Vacuole: A vacuole is a membrane-bound sac that plays roles in intracellular digestion and the release of cellular waste products. In animal cells, vacuoles are generally small. Vacuoles tend to be large in plant cells and play several roles: storing nutrients and waste products, helping increase cell size during growth, and even acting much like lysosomes of animal cells. Central Vacuole (only in plant cells) The plant cell vacuole also regulates turgor pressure in the cell. Water collects in cell vacuoles, pressing outward against the cell wall and producing rigidity in the plant. Without sufficient water, turgor pressure drops and the plant wilts.Storage space for water and other substances (e.g. toxins that deter predators from eating it) Most mature plant cells have one large central vacuole that typically occupies more than 30% of the cell's volume, and that can occupy as much as 80% of the volume for certain cell types and conditions Websites: http://www.cellsalive.com/cells/cell_model.htm http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vacuole