* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Diffusion, Osmosis, and Active Transport
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
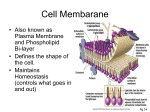
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
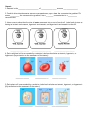
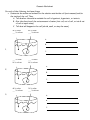
Name ___________________________________ P. ____ Diffusion Worksheet 1. Use arrows to indicate the direction of diffusion in each case: cell membrane. is a cell membrane. A) is a molecule that can pass through the B) 2. For each of the situations below use an arrow to indicate the net movement of sugar into or out of the cell. (Assume that the sugar molecules can pass through the cell membrane in each case.) 1% sugar 3% sugar 1% sugar 5% sugar 1% sugar 1% sugar 3. The cell membrane is made of a ___________________ ______________________. 4. The cell membrane is ___________________________permeable. This means that ____________ ______________________________________________________________________. 5. Diffusion always causes particles to move from a region of _______________ concentration to a region of ______________ concentration. 6. Does a cell expend energy when molecules diffuse in or out of the cell? _____________ 7. Moths emit (give off to the air) chemicals called pheromones to attract a mate. a) Which process is responsible for the distribution of these chemicals through the air? b) If a moth detects pheromones, how might it figure out which direction they are coming from? Osmosis 1. Osmosis is the ____________________ of _______________ across a ______________. 2. In which direction does water move across membranes, up or down the concentration gradient? It moves _________ the concentration gradient from a _______ concentration to a _________ concentration. 3. Use arrows to show the direction of water movement into or out of each cell. Label each picture as having an isotonic environment, hypotonic environment, and hypertonic environment to the cell. _______________________ ________________________ _________________________ 4. Each red blood cell is surrounded by a solution. Label each solution as isotonic, hypotonic, or hypertonic (Pay attention to the movement of the water): _____________ _____________ ______________ 5. Each plant cell is surrounded by a soulution. Label each solution as isotonic, hypotonic, or hypertonic (Pay attention to the movement of the water): ______________ ____________ ________________ Osmosis Worksheet For each of the following, do these things. Determine the solute and solvent for the solution outside the cell (environment) and for the inside of the cell. Then… A. Tell whether the solution outside the cell is hypotonic, hypertonic, or isotonic. B. Give the direction of the net movement of water (into cell, out of cell, or into & out of cell at equal rates). C. Tell what will happen to the cell (shrink, swell, or stay the same). 20 % solute ___ % solvent 80 % solute ___ % solvent A. B. 1. C. ___ % solute 10 % solvent ___ % solute 90 % solvent A. 2. B. C. 40 % solute ___ % solvent 3. 30 % solute ___ % solvent A. B. C.