* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Passive Transport + Potato lab
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
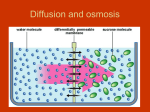
Lesson 10 February 1st, 2011 Review of Passive Transport Simple Diffusion Particles will move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until equilibrium is met. Facilitated Diffusion Channels that allow larger particles to pass across the membrane Osmosis the net movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Terms used to describe solutions. Solution a homogeneous mixture composed of two or more substances. A solute is dissolved in another substance, known as a solvent. The solvent does the dissolving. Example: Water The following terms are used to compare two solutions separated by a semi-permeable membrane. The water moving into or out of the cell is driven by the osmotic pressure caused by concentration gradients. Isotonic solution – a solution of equal solute concentration Equal parts of water move in and out of the cell. The water pressure inside the cell remains the same. Hypertonic solution – a solution that has higher solute concentration than some other solution Water will move from the area of low concentration in the cell to high concentration in the solution The water pressure inside the cell will decrease. Hypotonic solution – a solution that has a lower solute concentration than some other solution. Water will move from the low concentration solution to the high concentration cell. The water pressure in the cell will increase. Under normal conditions, osmosis does not occur into or out of red blood cells. The cells maintain their normal size and shape. If the solute has a lower concentration of solute than blood serum (hypotonic solution), it may dilute the blood serum until it is hypotonic to blood cell cytoplasm. If this occurs, osmosis will occur into the red blood cells, causing the cells to swell and in some cases burst which can be fatal as the cell can no longer transport oxygen. This is called hemolysis. If the solute has a higher concentration of solute than blood serum (hypertonic solution), it may concentrate blood serum until it is hypertonic to blood cell cytoplasm. Osmosis will occur out of the blood cells, causing the blood cells to become small and scalloped shaped. This shape is dangerous as the cells tend to stick together and clog arteries and veins, which prevents oxygen from reaching tissues. This condition is called crenation, and may also be fatal. Osmosis Lab 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 1. Read over lab Make the solutions needed. Cut up, measure and weigh the potato slices. Wait a few days Weigh and measure the potato slices Answer the questions