* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Transport (Diffusion and Osmosis)
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
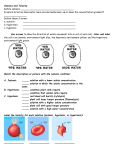
Transport Across Plasma Membranes (Diffusion and Osmosis) • The cell’s inner pool is called: Intracellular fluid. • In a multicellular organism, the fluid outside the cell is extracellular fluid. • Movement between fluid compartments are governed in part by gradients, differences in the concentration of materials in one part compared to those in another. Two Kinds of Transport: • 1. Passive (Diffusion): materials move from regions of higher concentration to regions of lower concentration, without energy expenditure by the cell. • 2. Active: movement of substances against concentration gradients (from low to high), requiring the expenditure of energy by the cell. Passive Transport and the Movement of Water (Osmosis) Water moves from a region of higher water concentration to a region of lower water concentration. Solution (Solute and Solvent) • Solute: a substance that has been dissolved in a solvent. • Solvent: a substance capable of dissolving other molecules. Solutions can be: • Isotonic: two solutions having the same concentration of solutes. • Cells placed in isotonic solutions maintain their shapes. • Hypotonic: having a lower concentration of solutes than another solution. • Cells swell in hypotonic solutions. • Hypertonic: having a higher concentration of solutes than another solution. • Cells shrink in hypertonic solutions. True-false questions 1. A cell placed in an isotonic solution will swell. 2. A cell placed in hypertonic solution will swell. 3. A cell placed in hypotonic solution will swell. Answers • 1. F • 2. F • 3. T