* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Snork Activity
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
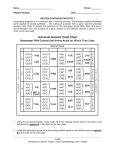
Name: ______________________________________ Per: _______ Date: _____________ Simulating Protein Synthesis to create a SNORK! Read the following to help you complete a successful SNORK organism. Genes are the units that determine inherited characteristics such as hair color as blood type. Genes consist of DNA molecules that code for the proteins our cells make. The sequence of nucleotides (and therefore the sequence of bases) in DNA determines the sequence of amino acids in proteins. The sequence of DNA is the most important part of determining what proteins are synthesized. During transcription, which takes place in the nucleus of the cell, messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules are built along the DNA sequence into a single RNA strand. mRNA leaves the nucleus and travels to the ribosome where proteins are made. The 3-base codons in the mRNA strand will pair up with anti-codons on the transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules. Each tRNA carries an amino acid to the ribosome, and these amino acids link together to form a protein. The amino acids are bound together by peptide bonds and form a polypeptide. The process in which the original DNA information (carried by the mRNA) is transferred into a protein is called translation. In this investigation you will simulate the process of transcription and translation to create the proteins that will develop the characteristic traits of your SNORK. What is a SNORK? It is a simple organism that contains only one chromosome. This chromosome is made up of 9 genes (A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I). Each gene is responsible for a certain trait of the organism. What does a SNORK look like? Well, that’s for you to show us! PROCEDURE: 1. To determine the trait for Gene A of your SNORK, notice the sequence of nucleotides in the DNA. On the line provided, write the sequence of nucleotides of mRNA that are complementary to DNA (this step represents transcription). 2. In order to determine the sequence of amino acids, use the codon chart to determine your amino acid sequence, and record this in the data table (this step represents translation). 3. Using the trait chart, find the trait that matches the amino acid sequence. Record the information in the data table. 4. Repeat the steps for the remaining genes (B through F). 5. Complete the analysis questions and create a drawing of your SNORK. All SNORK should contain school appropriate distinguishing marks. NO INAPPROPRIATE PARTS. SNORK GENETIC TRAITS Amino Acid Sequence Trait Tryptophan, Proline, Isoleucine, BLACK SPOTS Tryptophan, Valine, Isoleucine STRIPES Asparagine, Alanine FOUR LEGS Lysine, Alanine THREE LEGS Proline, Serine, Phenylalanine, Glycine LONG TAIL Valine, Serine, Phenylalanine, Glycine NO TAIL Lysine, Phenylalanine CURLY HAIR Lysine, Tyrosine STRAIGHT HAIR Proline, Glutamine, Alanine RED SKIN Proline, Glutamine, Glutamine GREEN SKIN Threonine, Threonine, Aspartate MALE (baseball cap) Threonine, Threonine, Leucine FEMALE (bow in hair) Serine, Histidine, Proline THREE ARMS Serine, Arginine, Proline FIVE ARMS Valine, Lysine, Tyrosine ONE EYE Proline, Lysine, Leucine THREE EYES Threonine, Glycine, Phenylalanine FOUR TEETH Tryptophan, Alanine, Phenylalanine NO TEETH Analysis Questions: 1. What part of DNA is the most important in determining what proteins are synthesized? 2. What is the role of ribosomes in creating proteins? 3. What is the name of the bond that holds amino acids together? 4. What is the name of the triplet sequence on tRNA (see picture to the right)? 5. What is the name of the triplet sequence found on mRNA that tRNA binds to? 6. What is the name of the triplet sequence that CODES for the amino acid? What RNA molecule is it found on? 7. Complete the Venn Diagram about transcription and translation. Put at least two pieces of information in each of the three areas. TRANSCRIPTION TRANSLATION 8. Suppose you knew the makeup of specific proteins in a cell. How would you determine the particular DNA code that coded for them? (Hint: Given the trait, how would you find the DNA) 9. How could one change in a DNA nucleotide alter the formation of the translated protein? An example would be the difference between normal and sickle-cell hemoglobin) Draw your SNORK Below: Name: __________________________________________________ Date: ________________ Period: _____ SNORK #1 Transcribe and translate the following DNA codes to find out what characteristics your SNORK has. Use the charts provided to determine the amino acid sequence and the protein traits of your SNORK. Once you have determined the traits of your SNORK, draw a picture in the space provided, then answer the questions in the packet. Gene A DNA: ACC CAT TAT Gene B Gene C DNA: TTG CGA DNA: TTT ATG mRNA ______________________ mRNA ______________________ mRNA _____________________ Amino Acid Sequence Amino Acid Sequence Amino Acid Sequence ____________________________ _____________________________ ____________________________ Trait _______________________ Trait ________________________ Trait _______________________ Gene D DNA: GGA GTT CGA Gene E DNA: GGG AGG AAA CCC Gene F DNA: TGT TGT CTA mRNA ______________________ mRNA ______________________ mRNA _____________________ Amino Acid Sequence Amino Acid Sequence Amino Acid Sequence ____________________________ _____________________________ ____________________________ Trait _______________________ Trait ________________________ Trait _______________________ Gene G DNA: AGT GTA GGT Gene H DNA: GGT TTT GAC Gene I DNA: TGA CCT AAA mRNA ______________________ mRNA ______________________ mRNA _____________________ Amino Acid Sequence Amino Acid Sequence Amino Acid Sequence ____________________________ _____________________________ ____________________________ Trait _______________________ Trait ________________________ Trait _______________________ Name: __________________________________________________ Date: ________________ Period: _____ SNORK #2 Transcribe and translate the following DNA codes to find out what characteristics your SNORK has. Use the charts provided to determine the amino acid sequence and the protein traits of your SNORK. Once you have determined the traits of your SNORK, draw a picture in the space provided, then answer the questions in the packet. Gene A DNA: ACC CAT TAT Gene B Gene C DNA: TTC CGA DNA: TTT AAA mRNA ______________________ mRNA ______________________ mRNA _____________________ Amino Acid Sequence Amino Acid Sequence Amino Acid Sequence ____________________________ _____________________________ ____________________________ Trait _______________________ Trait ________________________ Trait _______________________ Gene D DNA: GGA GTT GTT Gene E DNA: CAT AGG AAA CCC Gene F DNA: TGT TGT AAT mRNA ______________________ mRNA ______________________ mRNA _____________________ Amino Acid Sequence Amino Acid Sequence Amino Acid Sequence ____________________________ _____________________________ ____________________________ Trait _______________________ Trait ________________________ Trait _______________________ Gene G DNA: AGT GTA GGT Gene H DNA: CAT TTC ATA Gene I DNA: ACC CGC AAG mRNA ______________________ mRNA ______________________ mRNA _____________________ Amino Acid Sequence Amino Acid Sequence Amino Acid Sequence ____________________________ _____________________________ ____________________________ Trait _______________________ Trait ________________________ Trait _______________________ Name: __________________________________________________ Date: ________________ Period: _____ SNORK #3 Transcribe and translate the following DNA codes to find out what characteristics your SNORK has. Use the charts provided to determine the amino acid sequence and the protein traits of your SNORK. Once you have determined the traits of your SNORK, draw a picture in the space provided, then answer the questions in the packet. Gene A DNA: ACC GGA TAT Gene B Gene C DNA: TTC CGA DNA: TTT ATG mRNA ______________________ mRNA ______________________ mRNA _____________________ Amino Acid Sequence Amino Acid Sequence Amino Acid Sequence ____________________________ _____________________________ ____________________________ Trait _______________________ Trait ________________________ Trait _______________________ Gene D DNA: GGA GTT GTT Gene E DNA: CAT AGG AAA CCC Gene F DNA: TGT TGT CTA mRNA ______________________ mRNA ______________________ mRNA _____________________ Amino Acid Sequence Amino Acid Sequence Amino Acid Sequence ____________________________ _____________________________ ____________________________ Trait _______________________ Trait ________________________ Trait _______________________ Gene G DNA: AGT GCC GGT Gene H DNA: GGT TTT GAC Gene I DNA: ACC CGC AAG mRNA ______________________ mRNA ______________________ mRNA _____________________ Amino Acid Sequence Amino Acid Sequence Amino Acid Sequence ____________________________ _____________________________ ____________________________ Trait _______________________ Trait ________________________ Trait _______________________