* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Membrane aka Plasma Membrane
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Theories of general anaesthetic action wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
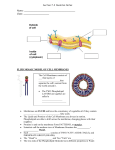
Membrane Transport Pages 78-85 include information on membrane transport Cell Membrane aka Plasma Membrane • Composed of double layer of phospholipids and • • • proteins (A phospholipid bilayer) Surrounds outside of ALL cells Is semipermeable Watch This Outside of cell Proteins Carbohydrate chains Cell membrane Inside of cell (cytoplasm) Protein channel Lipid bilayer 2 Phospholipids • Heads contain glycerol & • • • phosphate and are hydrophilic (attract water) Tails are made of fatty acids and are hydrophobic (repel water) Make up a bilayer where tails point inward toward each other Can move laterally to allow small molecules (O2, CO2, & H2O to enter) copyright cmassengale 3 The Cell Membrane is Fluid FLUID MOSAIC MODEL: Molecules in cell membranes are constantly moving and changing 4 Cell Membrane Proteins • Proteins help move large • • molecules or aid in cell recognition Peripheral proteins are attached on the surface (inner or outer) Integral proteins are embedded completely through the membrane copyright cmassengale 5 GLYCOPROTEINS Recognize “self” Glycoproteins have carbohydrate tails to act as markers for cell recognition copyright cmassengale 6 Cell Membrane in Plants Cell membrane • Lies immediately against the cell wall in plant cells • Pushes out against the cell wall to maintain cell shape copyright cmassengale 7 Cell Membrane Forming Spontaneously?! Remember The Heterotroph Hypothesis? Two Forms Of Membrane Transport Concepts: Equilibrium Concentration gradients Polarity Molecule size Electrical Charge Passive vs. Active Passive Transport Passive transport requires no energy! Diffusion - Movement from [hi] to [low] Osmosis - Diffusion of water Facilitated Diffusion - with carrier proteins Active Transport Active transport requires energy Ion Channels Ion Pumps Endocytosis Phagocytosis Pinocytosis Exocytosis