* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BIO 2310 - MSU Denver
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
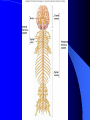
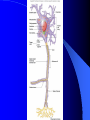
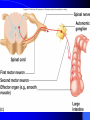
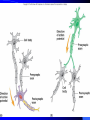
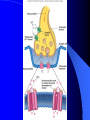
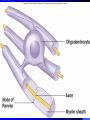
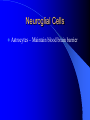
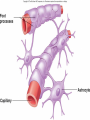
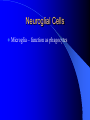
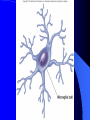
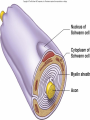
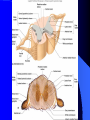
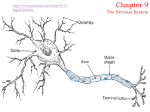
Nervous System General functions: Sensory – receptors Integration & stores information as memory Response – motor – effectors Classification Central Nervous System – brain & spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System – Afferent Somatic Visceral – Efferent Somatic Visceral = Autonomic Nervous System Classification Autonomic Nervous System – Sympathetic Nervous System for fight or flight response – Parasympathetic Nervous System for rest and relaxation response Key Points Classify the Autonomic Nervous System CNS or PNS Afferent or Efferent Sensory or Motor Somatic or Visceral Neuron = Nerve Cell Cell body – Ganglion – Nucleus Cytoplasmic processes – Axon = Fiber Fiber tracts in CNS Nerve in PNS Sensory, Motor, Mixed – Dendrite Synapse Junction between adjacent neurons [Telodendria – ends of axon] Neurotransmitters – chemicals bridging the synapse Neuroglia = Nerve glue Supportive cells to neurons Ependymal cells – line the neurocoel and provide nutrients Neuroglial Cells Oligodendroglia – produce myelin in CNS which is white and speeds up nerve impulse transmission Neuroglial Cells Astrocytes – Maintain blood brain barrier Key Points Parkinson’s Disease in humans is known to be caused by a decrease in dopamine (neurotransmitter) in the brain. Why not just inject patients with IV dopamine? Neuroglial Cells Microglia – function as phagocytes Key Points What is a phagocyte? Neuroglial Cells Schwann Cells – Produce myelin in PNS Key Points What is meant by white matter? What is meant by gray matter? Development of Nervous System Neurulation Neural tube – Germinal layer – medial, with mitosis – Mantle layer – gray, cell bodies of neurons – Marginal layer – white – cytoplasmic processes without nuclei Development of Nervous System Neuroblasts form neurons Spongioblasts form neuroglia Alar plate is dorsal gray matter (nuclei) Basal plate is ventral gray matter