* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Protein phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Type three secretion system wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
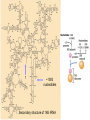
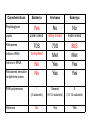
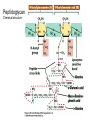
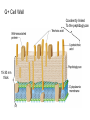
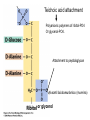
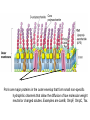
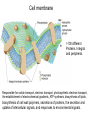
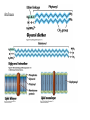
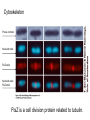
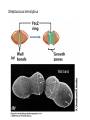
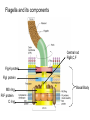
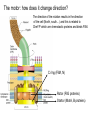
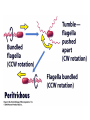
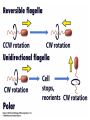
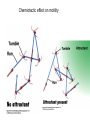
Fisiología microbiana Bota 6006 eee- e- endoespora flagelo Thiomargarita namibiensis tallo células hijas (1-7) Bdellovibrio 1mm 1 ~1500 nucleotides Secondary structure of 16S rRNA Evolutionary distance - # de nucleótidos diferentes y se usan para calcular distancia. Maximum parsimony - # de nucleótidos diferentes, sus posiciones y la naturaleza de las diferencias. EL ARBOL DE LA VIDA basado en secuencias de genes de RNA ribosomal 16S • la raíz del árbol de la vida representa una forma ancestral común • Tres linajes distintivos (2 Prokarióticos/1 Eucariótico) Archaea, Bacteria & Eucaria • Archaea & Eucaria son evolutivamente más relacionados •Archaea están evolutivamente más cercanas a la forma ancestral (más primitivos). • Eucariotas están más distanciados de la forma ancestral (más evolucionados) • origen termofílico de los seres vivos Caracteristicas Peptidoglycan Lipids Ribosomes Initiator tRNA Introns in tRNA Ribosomes sensitive to diphteria toxins RNA polymerase Histones Bacteria Archaea Eukarya Yes No No Ester linked Ether linked Ester linked 70S No No 70S Met Yes Yes 80S Met Yes Yes 1 (4 subunits) Several (8-12 subunits) 3 (12-14 subunits) No Yes Yes formyl-Met Prokaryotic cell wall The primary function of the CW is to protect the cell from bursting. There are only two types of CW in Bacteria: Peptidoglycan Chemical structure G+ Cell Wall Covalently linked To the peptidoglycan 15-30 nm thick Teichoic acid attachment Polyanionic polymers of ribitol-PO4 Or glycerol-PO4. Attachment to peptidoglycan N-acetil ácido murámico (mureína) or glycerol LPS It produce a permeability barrier to hydrophobic compounds: antibiotics, dyes (eosin-methylene blue), bile salts Polisacárido O-específico desata reacciones alérgicas Polisacárido medular Lipido A Endotoxina, fiebre, necrotización de tejidos fallo cardíaco Porin are major proteins in the outer envelop that form small non-specific hydrophilic channels that allow the diffusion of low molecular weight neutral or charged solutes. Examples are LamB, OmpF, OmpC, Tsx. Periplasm It is a aqueous compartment containing protein, salts, oligosaccharide, and peptidoglycan. What happens in this space? Specialized activities such as 1) oxidation-reduction reactions 2) osmotic regulation 3) solute transport 4) protein secretion 5) degradation by phosphatases and nucleases. 6) Detoxification Cell membrane >100 different Proteins. Integral and peripheral. Responsible for solute transport, electron transport, photosynthetic electron transport, the establishment of electrochemical gradients, ATP synthesis, biosynthesis of lipids, biosynthesis of cell wall polymers, secretions of proteins, the secretion and uptake of intercellular signals, and responses to environmental signals. Ácidos grasos Rol estructural en la membrana citoplasmica Archaea Cytoskeleton Phase contrast Nucleoid stain FtsZ stain Nucleoid stain FtsZ stain FtsZ is a cell division protein related to tubulin. Streptococcus hemolyticus Wall band Cell Shape Rod-shape Bacterial Flagella amfitrico perítrico lofótrico monotrico Los flagelos son filamentos helicoidales y rígidos de un diámetro de ~20nm y que rota como una hélice. Estos consisten de: basal body, a hook, filament, motor, switch, export apparatus, capping and junction proteins. Flagella and its components Central rod FlgB,C,F FlgH protein FlgI protein MS ring FliF protein C ring Basal Body The motor H+ pass across the CM thru the MotA,B which provide the torque to rotate the rotor. C ring (FliM, N) Rotor (FliG proteins) Startor (MotA, B proteins) The motor: how does it change direction? The direction of the rotation results in the direction of the cell (North, south…) and this is related to CheY-P which are chemotactic proteins and binds FliM. C ring (FliM, N) Rotor (FliG proteins) Startor (MotA, B proteins) Chemiotactic effect on motility The motor FliC is not identical in all bacteria. 20 to 65 kD more importantly only the C and N-terminal seem to be conserved (~60%). The filament grows from the hook To the capping protein by adding flagellin monomers as it needs. Furthermore, a cell could have more than one type of flagellin. E. coli (1), Caulobacter sp. (3). Summary of steps in Flagella biosynthesis Gram-negative Bacteria