* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5.genome-browsers
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) wikipedia , lookup
Adeno-associated virus wikipedia , lookup
Segmental Duplication on the Human Y Chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Transposable element wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Whole genome sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Human Genome Project wikipedia , lookup
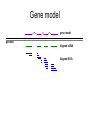
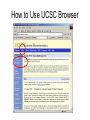
Bioinformatics Workshop 2 Identifying Unknown Genes … • Open a web browser and type in the URL: – informatics.gurdon.cam.ac.uk/online/workshops – Bookmark this page • Click on the link to the file: – useful-websites.html – Bookmark this page too – It also contains links to the example sequence files used in the workshop, and the presentations themselves Genome Browsers Now that most model organisms have had their genomes sequenced, we can get a lot more information about how the gene works, than by just doing a BLAST search against the protein databases. Even if ‘your’ favourite genome is still just in ‘scaffolds’ and not yet assembled into chromosomes, we can still add a lot of value. The main tasks that one does to a genome before releasing it to the user community is to annotate it. In practice this means adding gene models, based on known expressed sequences, both in the same organism and other fairly closely related ones, and possibly also purely predicted ones based on sequence composition analysis and ‘features’ like start and stop codons, and splice sites. And then known mapping markers, SNPs, etc, etc. With ~3,000,000,000 nucleotides in the genome sequence (human) this present a considerable challenge to display on a web browser page, which is of course the preferred option. Most genome browsers (software designed to display genome based data in a web broswer) have taken roughly the same approach, which we’ll take a quick look at… Gene model gene model genome Aligned cDNA Aligned ESTs Schematic Genome Browser Mus musculus, chromosome 12 navigate 24000 genome TRACKS Your sequence Genes ESTs 25000 26000 zoom + 27000 How to Use UCSC Browser 1. Exercises Find the web site for the Santa Cruz Genome Browser (sometimes called the Golden Path), and investigate the three genes for which you have the full length cDNA sequence, or the protein sequence, in the file example-sequences.html >TNeu084i05 How many exons does the gene appear to have? Has it been mapped already? Are there any likely upstream regulatory elements (look for conservation across species)? Are there other genes near by? >TGas122d03 Is this a relatively unique gene, or a member of a gene family? What can we learn from the comparison with human genes? Are there any differences between the gene model predicted from your cDNA, and the existing predictions? >hsp70-5 Starts with the protein sequence. How might this be better? Exercise 1. Results >TNeu084i05 Exercises 2. Now go to the two other main genome browsers, Ensemble and NCBI – find the Xenopus genome, and see if you get the same sort of functionality from them. Use the same two sequences. Are there different features? Are they easier/harder to use?