* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 04/03
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 wikipedia , lookup
Transposable element wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Real-time polymerase chain reaction wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Expression vector wikipedia , lookup
Histone acetylation and deacetylation wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
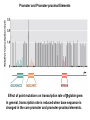
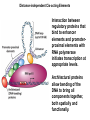
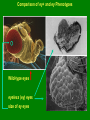
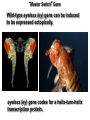
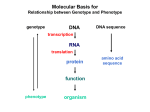
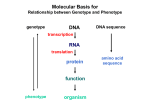
Molecular Basis for Relationship between Genotype and Phenotype genotype DNA DNA sequence transcription RNA translation protein function phenotype organism amino acid sequence Cis-acting Regulatory Elements Promoter - located near transcription-initiation site - binds RNA polymerase II Promoter-proximal Elements - located near promoter - binds proteins that assist RNA polymerase binding Distance-independent Elements - enhancers: increase transcription rates - silencers: decrease transcription rates Promoter and Promoter-proximal Elements In all cells, constitutive expression of transcription factors that bind to upstream promoter elements ensures active transcription at all times. Promoter and Promoter-proximal Elements Effect of point mutations on transcription rate of b-globin gene. In general, transcription rate is reduced when base sequence is changed in the core promoter and promoter-proximal elements. Distance-independent Cis-acting Elements Both enhancers and silencers affect transcription rate. Each has unique DNA sequence for the binding of regulatory proteins. Enhancer sequences contain multiple binding sites for trans-acting regulatory proteins. Enhancers could be located upstream from the promoter, downstream from the gene, or even within an intron of a gene. Distance-independent Cis-acting Elements Interaction between regulatory proteins that bind to enhancer elements and promoterproximal elements with RNA polymerase initiates transcription at appropriate levels. Architectural proteins allow bending of the DNA to bring all components together, both spatially and functionally. Regulatory Proteins that Modulate Transcription These proteins contain one or more functional domains: 1. Recognize DNA regulatory sequence 2. Interact with transcriptional apparatus proteins (RNA polymerase, proteins associated with RNA polymerase) 3. Interact cooperatively with other regulatory proteins bound to DNA sequence 4. Influence chromatin condensation 5. Act as sensor of intracellular physiological conditions Transcription Factors Transcription factors have: 1. DNA binding domain (interact with promoter-proximal elements or enhancers/silencers) 2. Transactivation domain (activate or repress transcription, involved in protein/protein interaction) Structural Families of Transcription Factors and Regulatory Proteins: Helix-Turn-Helix: Many homeotic genes code for TF's of this class. Zinc-Finger: Many steroid hormone receptor protein TF's belong to this class. Leucine Zipper: Proto-oncogenes such as c-jun and c-fos are genes that encode TF's of this class. Helix-Loop-Helix: Certain proto-oncogenes and genes involved in differentiation encode TF's of this class. Structural Families of Transcription Factors and Regulatory Proteins: Zinc-Finger: Leucine Zipper: Helix-Loop-Helix: Tissue-specific Regulation of Transcription Regulated transcription depends on: - specific enhancer for gene(s) - enhancer-specific activator proteins - correct interaction between enhancer and activator Tissue-specific regulation requires that the enhancer-specific activator is present only in cells of that tissue type. ectopic expression: expression in an abnormal location “Master Switch” Gene Eye formation requires over 2000 genes. eyeless (ey) mutation causes small rudimentary eyes to form in Drosophila melanogaster. Small eyes (Sey, Pax-6) in mouse causes similar phenotype. Aniridia gene in human (lack of normal iris) shows considerable homology to ey gene. Comparison of ey+ and ey Phenotypes Wild-type eyes eyeless (ey) eyes size of ey eyes “Master Switch” Gene Wild-type eyeless (ey) gene can be induced to be expressed ectopically. eyeless (ey) gene codes for a helix-turn-helix transcription protein.