* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hox
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Transposable element wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Essential gene wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
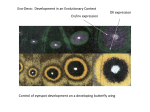
Evo-Devo: Evolutionary Development • DNA • Regulatory genes: code for signal proteins and transcription factor proteins – SP: target particular groups of cells for gene expression • Regulatory sequences: binding sites of transcription factors (enhancers, promoters). • Structural genes: Activated by binding of TF & RS • Responsible for producing phenotypic characters. Dll expression En/Inv expression Eyespots on a butterfly wing Homeotic Genes and Animal Body Plans • • • • • • Multicellular animals develop in four dimensions. 3 spatial + time Each cell has to have 1. information: where it is relative to other cells 2. where it is in the developmental sequence. Information provided by Homeotic genes (Hox genes) Cells along these major body axes assume positional information during development (After Strickberger.) Hox genes in Drosophila (body segmentation) Positional information Colinearity: 1. Expressed first 2. Anterior to posterior 3. Greater quantity of transcription factors Gene location in hox cluster Colinear Hox gene expression • Hox genes provide information on location. – 1. The transcription factor from the first Hox gene • required to express downstream Hox genes. – 2. The effectiveness in initiating sequential gene expression declines with distance. Paralogous and evolutionarily conserved • Each Hox gene contains a highly conserved 180 bp sequence – the homeobox. Codes for a DNA binding segment (aa sequence) in the transcription factor. The transcription factors activate structural genes. Structural genes produce structures appropriate for that location. Mutations in Hox genes result in inappropriate structures for that location. Hox gene products activate genes responsible for making a particular structure. Mutations in Hox genes Mutation of Hox gene antp bx, pbx, and abx Wings normally appear on T2 Hox mutations change identity of T3 cells to T2 cells. An extra pair of wings is produced. Ancestors of dipteran flies had 4 wings. Identity of a head segment changed to that of a thoracic segment Hox gene diversification diversification of animals • Hox paraloges (homologs): in everything from SpongeBob Squarepants to humans to fungi and plants (MADS-box genes). • Therefore, Homeobox genes predate the origin of animals. Representative arthropods: What is the basis of their diversity? 1 million sp. described; maybe 50 million still to be named. Exoskeleton; segmented body (H –T – A) and segmented legs Paired appendages on body segments; open circulatory system Crustaceans Hexapods Myriapods Chilicerates An onychophoran (velvet worm) Closest living relative of arthropods 1 pr. unjointed legs on each of the similar body segments Evolutionary diversification of arthropods partly based on sites of Hox gene expression Hox cluster of 9 loci for all arthropods abdA always expressed on ventral side of segment Evolutionary change in where a Hox gene is expressed Ubx and abdA not expressed in posterior segments Mutation: legless abdominal segments Homeotic genes and Flower formation C. 300,000 sps. of Angiosperms Four concentric whorls of modified leaves Normal order: sepals, petals, stamens, carpels MADS-box mutants (Hox genes)