Genes Involved in the Uptake and Catabolism of
... glycerol in the presence of gluconate, took up isotope from sodium [U-14C]gluconate at only very low rates, and cell-free extracts were devoid of gluconate kinase activity. In contrast, other Ppc+ transductants from the initially gluconate-tolerant ppc mutants, whose growth on a variety of hexoses a ...
... glycerol in the presence of gluconate, took up isotope from sodium [U-14C]gluconate at only very low rates, and cell-free extracts were devoid of gluconate kinase activity. In contrast, other Ppc+ transductants from the initially gluconate-tolerant ppc mutants, whose growth on a variety of hexoses a ...
Genes Involved in the Uptake and Catabolism of
... glycerol in the presence of gluconate, took up isotope from sodium [U-14C]gluconate at only very low rates, and cell-free extracts were devoid of gluconate kinase activity. In contrast, other Ppc+ transductants from the initially gluconate-tolerant ppc mutants, whose growth on a variety of hexoses a ...
... glycerol in the presence of gluconate, took up isotope from sodium [U-14C]gluconate at only very low rates, and cell-free extracts were devoid of gluconate kinase activity. In contrast, other Ppc+ transductants from the initially gluconate-tolerant ppc mutants, whose growth on a variety of hexoses a ...
An investigation of sympatric speciation in diploid organisms by
... genetic mechanisms of reproduction. In this methodology there is no direct comparison with biological data but the simulation follows, as closely as possible, natural genetic mechanisms of reproduction. The selected modelling method uses a framework derived from Penna [1995] which represents individ ...
... genetic mechanisms of reproduction. In this methodology there is no direct comparison with biological data but the simulation follows, as closely as possible, natural genetic mechanisms of reproduction. The selected modelling method uses a framework derived from Penna [1995] which represents individ ...
Development of multiple interval mapping for mapping QTL in
... Genes determining a quantitative trait or regions on chromosomes underlying a quantitative trait (Geldermann, 1975) are called quantitative trait loci or QTL. Unlike the gene determining a Mendelian trait, an individual QTL usually has a small effect on a quantitative trait. The total effect (which ...
... Genes determining a quantitative trait or regions on chromosomes underlying a quantitative trait (Geldermann, 1975) are called quantitative trait loci or QTL. Unlike the gene determining a Mendelian trait, an individual QTL usually has a small effect on a quantitative trait. The total effect (which ...
Pest Control by the Introduction of a Conditional Lethal Trait on
... advance of gene technology, a release involving 10 Ð20 loci is conceivable. The multilocus problem is simple if the loci are in equilibrium. In this case the loci are in random association and gamete frequencies are simply the product of gene frequencies across loci. However, we are interested in th ...
... advance of gene technology, a release involving 10 Ð20 loci is conceivable. The multilocus problem is simple if the loci are in equilibrium. In this case the loci are in random association and gamete frequencies are simply the product of gene frequencies across loci. However, we are interested in th ...
Modular Skeletal Evolution in Sticklebacks Is Controlled by Additive
... ABSTRACT Understanding the genetic architecture of evolutionary change remains a long-standing goal in biology. In vertebrates, skeletal evolution has contributed greatly to adaptation in body form and function in response to changing ecological variables like diet and predation. Here we use genome- ...
... ABSTRACT Understanding the genetic architecture of evolutionary change remains a long-standing goal in biology. In vertebrates, skeletal evolution has contributed greatly to adaptation in body form and function in response to changing ecological variables like diet and predation. Here we use genome- ...
The yeast Sup35 protein is a translation termination factor with the
... altering translational read-through, suggesting that they are complex traits that require a contribution from other factors. For example, the strain Bsc783/4c [PSI+] grew better on media containing 150mM CsCl than its [psi-] derivative (Supplementary Fig. 2b, right). The CsCl resistance was eliminat ...
... altering translational read-through, suggesting that they are complex traits that require a contribution from other factors. For example, the strain Bsc783/4c [PSI+] grew better on media containing 150mM CsCl than its [psi-] derivative (Supplementary Fig. 2b, right). The CsCl resistance was eliminat ...
The monogenic primary dystonias
... on linkage mapping to regions apparently different from, yet in close proximity to or overlapping with the known loci DYT18, DYT10 and DYT8. Clinically, this group of movement disorders includes pure dystonias and dystonia plus syndromes. In addition, dyskinesias (paroxysmal dystonias), although phe ...
... on linkage mapping to regions apparently different from, yet in close proximity to or overlapping with the known loci DYT18, DYT10 and DYT8. Clinically, this group of movement disorders includes pure dystonias and dystonia plus syndromes. In addition, dyskinesias (paroxysmal dystonias), although phe ...
The KetelD Dominant-Negative Mutations Identify
... intriguing biological phenomena and raises questions about the origin and function of factors required for the initiation of a new life. What are those factors? Where and how are they made? What are their functions? It has long been known that most of the factors that are required during early embry ...
... intriguing biological phenomena and raises questions about the origin and function of factors required for the initiation of a new life. What are those factors? Where and how are they made? What are their functions? It has long been known that most of the factors that are required during early embry ...
GENETICS Lois E Brenneman, MSN, ANP, FNP, C Historical
... Mechanism of Meiosis: Stages of m eiosis lead to reduction of the chrom osom e num ber by half and to the production of functional gam etes. During the first m eiotic division, pairs of chrom osom es are separated from each other. In the male, the second m eiotic division results in form ation of fo ...
... Mechanism of Meiosis: Stages of m eiosis lead to reduction of the chrom osom e num ber by half and to the production of functional gam etes. During the first m eiotic division, pairs of chrom osom es are separated from each other. In the male, the second m eiotic division results in form ation of fo ...
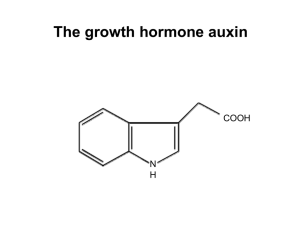
The growth hormone auxin
... The AUX/IAA genes • Transcription is rapidly induced by auxin • Independent of protein synthesis - primary response • Induced by cycloheximide • Unstable nuclear proteins • Large gene family (29 in Arabidopsis) AUX/IAA proteins probably serve as negative regulators ...
... The AUX/IAA genes • Transcription is rapidly induced by auxin • Independent of protein synthesis - primary response • Induced by cycloheximide • Unstable nuclear proteins • Large gene family (29 in Arabidopsis) AUX/IAA proteins probably serve as negative regulators ...
Alternatively Spliced Genes
... Evolutionarily, the basic machinery for pre-mRNA splicing appears to be highly conserved among different species of metazoans. In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, although only a small percentage of genes undergo splicing, more than 100 genes have been identified that are either dedicated to or involved in ...
... Evolutionarily, the basic machinery for pre-mRNA splicing appears to be highly conserved among different species of metazoans. In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, although only a small percentage of genes undergo splicing, more than 100 genes have been identified that are either dedicated to or involved in ...
Mutational Analysis of the Drosophila Sister-Chromatid
... imperative that sisterchromatid cohesionbe regulated precisely, the natureof the physical association between sisters is poorly understood. In addition, very little is known about the molecules that control temporal and spatial changes in cohesion, allowing chromosomes to separate from each other at ...
... imperative that sisterchromatid cohesionbe regulated precisely, the natureof the physical association between sisters is poorly understood. In addition, very little is known about the molecules that control temporal and spatial changes in cohesion, allowing chromosomes to separate from each other at ...
Genetics fill in review
... 40. Nucleotide segments of a DNA molecule that make up genes and are actually expressed in the phenotype of an organism are called ____________________. 41. Portions of genes that actually get translated into proteins are called ____________________. 42. Genes may be made more accessible to RNA poly ...
... 40. Nucleotide segments of a DNA molecule that make up genes and are actually expressed in the phenotype of an organism are called ____________________. 41. Portions of genes that actually get translated into proteins are called ____________________. 42. Genes may be made more accessible to RNA poly ...
Dominant and Recessive Inheritance Patterns of
... and were maintained under 16:8 L:D conditions at 25 °C. During the last quiescent stage, a single adult male of the opposite strain was placed on the leaf for at least 24 h so that the mites could copulate. Adult females were transferred onto a new piece of leaf every day until day 7. The progeny wa ...
... and were maintained under 16:8 L:D conditions at 25 °C. During the last quiescent stage, a single adult male of the opposite strain was placed on the leaf for at least 24 h so that the mites could copulate. Adult females were transferred onto a new piece of leaf every day until day 7. The progeny wa ...
Epistasis

Epistasis is a phenomenon that consists of the effect of one gene being dependent on the presence of one or more 'modifier genes' (genetic background). Similarly, epistatic mutations have different effects in combination than individually. It was originally a concept from genetics but is now used in biochemistry, population genetics, computational biology and evolutionary biology. It arises due to interactions, either between genes, or within them leading to non-additive effects. Epistasis has a large influence on the shape of evolutionary landscapes which leads to profound consequences for evolution and evolvability of traits.