* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The growth hormone auxin
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
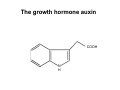
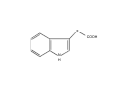
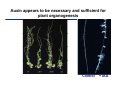
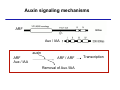
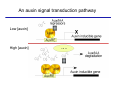
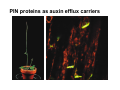
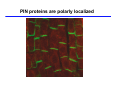
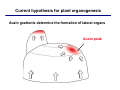
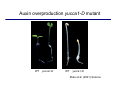
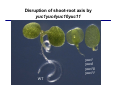
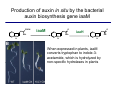
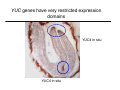
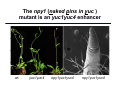
The growth hormone auxin COOH N H Discovery of auxin Auxin: the growth hormone water for 18 hours +IAA for 18 hours COOH N H The roles of auxin in plant growth and development •Root development •Vascular initiation and patterning •Flower development •Embryogenesis •Tropism Control + IAA Auxin appears to be necessary and sufficient for plant organogenesis Control + IAA Auxin functions are regulated at multiple levels 1. Auxin homeostasis (biosynthesis, conjugation, and degradation) 2. Auxin polar transport 3. Auxin signal transduction Approaches used for dissecting mechanisms of auxin actions 1. Biochemical approaches: characterization of auxin inducible genes AUX/IAA genes Auxin Response Element (AuxREs) Plants treated with water RNA isolation Plants treated with auxin RNA isolation The AUX/IAA genes • Transcription is rapidly induced by auxin • Independent of protein synthesis - primary response • Induced by cycloheximide • Unstable nuclear proteins • Large gene family (29 in Arabidopsis) AUX/IAA proteins probably serve as negative regulators Domain structures of AUX/IAA proteins I II III IV • degradation proteosome mediated • auxin promotes degradation • Domain II is important for stability The Auxin Response Elements 1. Analysis of the promoter regions of auxin inducible genes 2. Identify the conserved elements: TGTCTC 1. Construct an auxin reporter 2. Identify the transcription factors binding to the AuxREs Auxin reporter DR5 Cotyledons DR5-GFP auxin reporter Auxin response elements hypocotyl Root meristem GFP Gene Transcription factors bind to AuxREs Use AuxREs Cotyledons as a bait for yeast one hybrid screen Auxin response factors: 22 members in Arabidopsis hypocotyl Root meristem Approaches used for dissecting mechanisms of auxin actions 1. Biochemical approaches: characterization of auxin inducible genes AUX/IAA genes and ARFs (auxin response factors) 2. Genetic approaches: Identification and characterization of mutants resistant to exogenous auxin and auxin polar transport inhibitors. axr mutants, tir mutants Auxin resistance mutant screens + auxin auxin Two types of mutants: 1) Auxin uptake: aux1, axr4 2) Auxin response: axr1, axr2, axr3, axr5, axr6, tir1 Auxin resistance mutant screens Recessive: aux1, axr1,, axr4, axr5, axr6, msg1, tir1 Dominant: axr2, axr3, msg2, iaa28, Dominant axr mutants contain mutations in the domain II in Aux/IAA proteins AXR3/IAA17 axr3-1 axr3-3 axr3-1 axr3-3 Col-0 VVGWPPVR L G A plausible auxin signaling mechansim 1. Aux / IAA proteins are short lived and function as negative regulators 2. Mutations in Aux /IAA confer dominant auxin resistance; probably increase the half-life of Aux /IAA proteins 3. Auxin signaling may depend on the degradation of Aux / IAA proteins Auxin signaling mechanisms ARF Aux / IAA auxin ARF Aux / IAA ARF / ARF Removal of Aux /IAA Transcription Predictions from the model auxin ARF Aux / IAA ARF / ARF Transcription Removal of Aux /IAA 1. Inactivation of ARF should cause the same phenotypes as those induced by stabilized Aux/IAA 2. Inactivation of Aux/IAA should lead to auxinoverproduction phenotypes 3. Overexpression of ARF may suppress dominant Aux/IAA mutants Arabidopsis pattern mutants Basal mutant (mp, bdl) BDL encodes an Auxin / Indole-3-Acetic Acid protein (IAA12) MP encodes an auxin response factor (ARF5) How is Aux/IAA degraded? auxin ARF Aux / IAA ARF / ARF Transcription Removal of Aux /IAA Ubiquitin-mediated protein degradation machinery? An auxin signal transduction pathway Low [auxin] High [auxin] Previous genetic studies 1) The responses to excess exogenous auxin 2) Root elongation as a primary physiological readout 3) Known auxin mutants pin1 and pid are not auxin resistent Polar auxin transport Carrier mediated auxin transport Influx: a. passive b. AUX1 permease Efflux: Polarity set up by efflux carries if they are located only at the base PIN proteins as auxin efflux carriers PIN proteins are polarly localized Current hypothesis for plant organogenesis Auxin gradients determine the formation of lateral organs Auxin peak Auxin functions are regulated at multiple levels 1. Auxin biosynthesis 2. Auxin polar transport 3. Auxin signal transduction Auxin biosynthesis 1. Necessary for determining the physiological roles of auxin 2. Necessary for understanding auxin movements and dynamics 3. Provides genetic foundations for dissecting the mechanisms of auxin in plant development Proposed tryptophan dependent auxin biosynthetic pathways N NH2 N H N H N OH N H Nitrilase O COOH H COOH O N H NH2 N H N H OH N H Trp iaaM O NH2 N H O Hydrolase Auxin overproduction yucca1-D mutant WT yucca1-D WT yucca1-D Zhao et al. (2001) Science YUCCA encodes a flavin-monooxygenase involved in auxin synthesis O OH HN OH NH2 N OH O C NH2 N H Trp N N H YUCCA N H N H IOX N H Nitrilase OH N H Auxin Zhao et al. (2001) Science Overexpression of YUCCA genes causes auxin over-production Flower defects in yuc1yuc4 double mutants Disruption of shoot-root axis by yuc1yuc4yuc10yuc11 yuc1 yuc4 yuc10 yuc11 WT Can exogenous auxin rescue the yucca mutant phenotypes? 1. Auxin transport 2. Auxin gradient 3. The right dosage Production of auxin in situ by the bacterial auxin biosynthesis gene iaaM COOH O iaaM NH2 N H O iaaH NH2 N H OH N H When expressed in plants, iaaM converts tryptophan to indole-3acetamide, which is hydrolyzed by non-specific hydrolases in plants Complementation of yuc mutants by expressing the iaaM gene under the control of a YUCCA promoter A YUC promoter iaaM gene Transform yuc mutants Can the iaaM gene rescue yuc phenotypes? The yuc1yuc4 double mutant is rescued by the iaaM gene under the YUC1 promoter Proposed IAA biosynthetic pathway in plants Sugawara S. et.al. PNAS 2009;106:5430-5435 ©2009 by National Academy of Sciences YUC genes have very restricted expression domains YUC4 in situ YUC4 in situ Previous genetic studies 1) The responses to excess exogenous auxin 2) Root elongation as a primary physiological readout 3) Known auxin mutants pin1 and pid are not auxin resistent Genetic screens for yuc1yuc4 enhancers yuc1yuc4 The npy1 (naked pins in yuc ) mutant is an yuc1yuc4 enhancer wt yuc1yuc4 npy1yuc1yuc4 npy1yuc1yuc4 Analogous mechanisms between phototropic response and auxin-regulated organogenesis Developmental YUCCA signals auxin Blue light PHOT1 NPH3 Auxin transport (PIN3)? ARF7 / NPH4? Phototropic responses PID NPY1 Auxin transport (PIN1)? ARF5 / MP? Organogenesis Formation of pins is a hallmark for defects in auxin pathways wt pin1 pid mp Pin-like maize mutants wt ba1 spi1 Bif1 bif2 BARREN STALK1 (BA1) encodes a bHLH transcription factor SPARSE INFLORESCECNE1 (SPI1) encodes a YUC-like auxin biosynthesis enzyme BARREN INFLORESCENCE2 (BIF2) encodes a protein kinase involved in auxin transport and signaling. One of its targets for phosphorylation is BA1.