Engrailed cooperates with extradenticle and homothorax to repress
... et al., 1999; Shen et al., 1999). In mammals, a Hox-class (Antpclass) protein that is part of an endodermally expressed ParaHox cluster (Brooke et al., 1998; Leonard et al., 1993) has also been shown to interact functionally with mammalian homologs of Exd and Hth (Swift et al., 1998). In this work, ...
... et al., 1999; Shen et al., 1999). In mammals, a Hox-class (Antpclass) protein that is part of an endodermally expressed ParaHox cluster (Brooke et al., 1998; Leonard et al., 1993) has also been shown to interact functionally with mammalian homologs of Exd and Hth (Swift et al., 1998). In this work, ...
The Homothorax homeoprotein activates the nuclear localization of
... nucleus in all cells. The distribution of nuclear Exd (Aspland and White 1997) correlates with the functional requirement for exd, indicating that only the nuclear Exd can exert its function. In the embryonic midgut, Exd nuclear localization in the endoderm is regulated by Decapentaplegic (Dpp) and ...
... nucleus in all cells. The distribution of nuclear Exd (Aspland and White 1997) correlates with the functional requirement for exd, indicating that only the nuclear Exd can exert its function. In the embryonic midgut, Exd nuclear localization in the endoderm is regulated by Decapentaplegic (Dpp) and ...
PDF
... a trithorax group regulator. We propose that Utx is needed in the early embryo to prevent inappropriate instalment of long-term Polycomb repression at HOX genes in cells in which these genes must be kept active. In contrast to PRC2, which is essential for, and continuously required during, germ cell ...
... a trithorax group regulator. We propose that Utx is needed in the early embryo to prevent inappropriate instalment of long-term Polycomb repression at HOX genes in cells in which these genes must be kept active. In contrast to PRC2, which is essential for, and continuously required during, germ cell ...
From DNA to diversity: molecular genetics and the evolution of
... foremost among them is that biology first had to address another central genetic mystery a that is, which genes out of the thousands in any species control morphology? One of the most important biological discoveries of the past two decades is that most animals, no matter how divergent in form, shar ...
... foremost among them is that biology first had to address another central genetic mystery a that is, which genes out of the thousands in any species control morphology? One of the most important biological discoveries of the past two decades is that most animals, no matter how divergent in form, shar ...
Investigating the functional significance of evolutionarily conserved
... Bilaterans share a common anterior-posterior (A-P) axis that is patterned by the Homeotic selector (Hox) genes. In Drosophila melanogaster, Hox gene expression in spatially restricted domains along the A-P axis of the embryo determines segmental identity. Identifying the genetic mechanisms of HOX co ...
... Bilaterans share a common anterior-posterior (A-P) axis that is patterned by the Homeotic selector (Hox) genes. In Drosophila melanogaster, Hox gene expression in spatially restricted domains along the A-P axis of the embryo determines segmental identity. Identifying the genetic mechanisms of HOX co ...
CONSERVATION AND DIVERGENCE IN MOLECULAR
... Many organisms manifest polarity at some level; indeed, asymmetry seems essential for promoting meaningful interaction with the environment. Even the simplest unicellular organisms display temporary polarity in response to their environment; for example, in reception and response to chemotactic sign ...
... Many organisms manifest polarity at some level; indeed, asymmetry seems essential for promoting meaningful interaction with the environment. Even the simplest unicellular organisms display temporary polarity in response to their environment; for example, in reception and response to chemotactic sign ...
Maternal-Effect Genes That Alter the Fate Map of the Drosophila
... protein at normal levels. (d) wosrD/waP! All abdominal denticles are absent. sp, spiracles. (e) ezuPJ/ezuP< Note the anterior shift of the first ftz stripe (arrowhead), the abnormally wide second stripe, and the compression of the posterior stripes (bracket). (f) exupJ/exup< The pattern of thoracic ...
... protein at normal levels. (d) wosrD/waP! All abdominal denticles are absent. sp, spiracles. (e) ezuPJ/ezuP< Note the anterior shift of the first ftz stripe (arrowhead), the abnormally wide second stripe, and the compression of the posterior stripes (bracket). (f) exupJ/exup< The pattern of thoracic ...
Linköping University Post Print Segment-specific Neuronal Sub-type Specification by the Integration of
... A9, and Abd-B in segments A5 to A9 (Figures S1 and S2; Figure 2A and 2B). Thus, Bx-C gene expression fits with a potentially suppressive role on Ap cluster formation, Antp ...
... A9, and Abd-B in segments A5 to A9 (Figures S1 and S2; Figure 2A and 2B). Thus, Bx-C gene expression fits with a potentially suppressive role on Ap cluster formation, Antp ...
Embryonic development and the understanding of the adult body
... periodicity and thus are defining double segmental units rather than single segmental units (Chipman et al. 2004, Chipman & Akam 2008). This is probably most obvious from the expression of the Strigamia caudal (Stm-cad) and even-skipped (Stm-eve1) genes, which both are expressed in stripes in the un ...
... periodicity and thus are defining double segmental units rather than single segmental units (Chipman et al. 2004, Chipman & Akam 2008). This is probably most obvious from the expression of the Strigamia caudal (Stm-cad) and even-skipped (Stm-eve1) genes, which both are expressed in stripes in the un ...
(Japan), organized by Nori Satoh
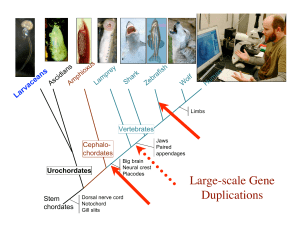
... events, such as rupture of the Hox-cluster, in the context of a new understanding of chordate phylogeny. (Cañestro and Postlethwait, 2007 Dev Biol) ...
... events, such as rupture of the Hox-cluster, in the context of a new understanding of chordate phylogeny. (Cañestro and Postlethwait, 2007 Dev Biol) ...
A nested deletion approach to generate Cre deleter mice with
... made this animal a valuable model for human development, physiology and diseases. Of particular interest is the loxP/Cre recombinase system, which allows for site- or time-specific recombination of particular target sequences, hence for a conditional approach of targeted genetic modifications (Sauer ...
... made this animal a valuable model for human development, physiology and diseases. Of particular interest is the loxP/Cre recombinase system, which allows for site- or time-specific recombination of particular target sequences, hence for a conditional approach of targeted genetic modifications (Sauer ...
Functional cooperation between the non-paralogous
... vertebrae of control skeletons (for iconography, see FromentalRamain et al., 1996). We have also used the following morphological landmarks, which showed little variation between control animals: (i) an L3 morphology was assigned to the most anterior vertebra exhibiting lateral processes extending b ...
... vertebrae of control skeletons (for iconography, see FromentalRamain et al., 1996). We have also used the following morphological landmarks, which showed little variation between control animals: (i) an L3 morphology was assigned to the most anterior vertebra exhibiting lateral processes extending b ...
Evolution of the vertebrate jaw: comparative embryology and
... genes in amniotes are arranged tandemly in four clusters, each of which is found on a different chromosome (reviewed by McGinnis & Krumlauf, 1992). There is a tendency called ‘spatial collinearity’ in that the genes located in the 3′ direction of a cluster are more likely to be up-regulated in the a ...
... genes in amniotes are arranged tandemly in four clusters, each of which is found on a different chromosome (reviewed by McGinnis & Krumlauf, 1992). There is a tendency called ‘spatial collinearity’ in that the genes located in the 3′ direction of a cluster are more likely to be up-regulated in the a ...
GENES AND DEVELOPMENTAL PATHWAYS
... b). It may be anticipated that pseudoallelic series affecting morphological traits, such as the case to be described below, can also be profitably exploited to learn more about how genes control developmental pathways. A number of levels of functional integration of the genetic material can now be r ...
... b). It may be anticipated that pseudoallelic series affecting morphological traits, such as the case to be described below, can also be profitably exploited to learn more about how genes control developmental pathways. A number of levels of functional integration of the genetic material can now be r ...
Knockdown of Parhyale Ultrabithorax - IMBB
... Ventral view scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of a wild-type Parhyale hatchling (A and B) and a hatchling of an embryo injected with PhUbx siRNAs (C and D). Anterior is toward the top. Higher magnifications of (A and C) are shown in (B and D) respectively. Appendage identity is indicated by color: ...
... Ventral view scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of a wild-type Parhyale hatchling (A and B) and a hatchling of an embryo injected with PhUbx siRNAs (C and D). Anterior is toward the top. Higher magnifications of (A and C) are shown in (B and D) respectively. Appendage identity is indicated by color: ...
Mice homozygous for a targeted disruption of Hoxd-3
... Fig. 4. Homeotic transformation of the atlas and axis vertebrae in Hoxd-3 mutant newborns. The skeletons were stained with alizarin red and alcian blue and cleared by treatment with alkali and trypsin. (A) A ventral view of the wild-type (+/+) craniocervical junction. (B) Ventral view of the same sk ...
... Fig. 4. Homeotic transformation of the atlas and axis vertebrae in Hoxd-3 mutant newborns. The skeletons were stained with alizarin red and alcian blue and cleared by treatment with alkali and trypsin. (A) A ventral view of the wild-type (+/+) craniocervical junction. (B) Ventral view of the same sk ...
Hox Targets and Cellular Functions
... one (T2), including the development of four wings in the thorax instead of the wildtype pattern of two wings and two halteres (small dorsal appendages of the T3 needed to fly) [30]; similarly, gain-of-function mutations in Antennapedia transform the antennae into legs [32–34]. In the mouse, the exis ...
... one (T2), including the development of four wings in the thorax instead of the wildtype pattern of two wings and two halteres (small dorsal appendages of the T3 needed to fly) [30]; similarly, gain-of-function mutations in Antennapedia transform the antennae into legs [32–34]. In the mouse, the exis ...
Novel regulatio pendage transformation
... legs). Therefore, the originally established second thoracic appendages/ first pereopods are false-coloured in green. The first thoracic tagma boundary between the second maxilla limbs (A) can be seen in their transformation to maxillipeds (B,C). (D,E) 25-30% and 7580% stage embryos stained with a p ...
... legs). Therefore, the originally established second thoracic appendages/ first pereopods are false-coloured in green. The first thoracic tagma boundary between the second maxilla limbs (A) can be seen in their transformation to maxillipeds (B,C). (D,E) 25-30% and 7580% stage embryos stained with a p ...
Altered cellular proliferation and mesoderm
... 2 week period. For activation assay, splenocytes were seeded at a concentration of 106 cells/ml in a 96-well plate. Cells were incubated in 200 µl of DME, 10% FCS, 10 mM Hepes pH 7.4 solution supplemented with 10 µg/ml of LypoPolySaccharide (LPS, Sigma). After 48 hours of incubation at 37°C, [3H]thy ...
... 2 week period. For activation assay, splenocytes were seeded at a concentration of 106 cells/ml in a 96-well plate. Cells were incubated in 200 µl of DME, 10% FCS, 10 mM Hepes pH 7.4 solution supplemented with 10 µg/ml of LypoPolySaccharide (LPS, Sigma). After 48 hours of incubation at 37°C, [3H]thy ...
Centipede Hox genes - Development
... developmental genetics facilitates this, as it provides some basis for speculating about the developmental processes of other arthropods. The body plan of Drosophila is encoded in part by the patterned expression of a set of transcription factors called the Hox proteins, which divide the embryo into ...
... developmental genetics facilitates this, as it provides some basis for speculating about the developmental processes of other arthropods. The body plan of Drosophila is encoded in part by the patterned expression of a set of transcription factors called the Hox proteins, which divide the embryo into ...
INTRODUCTION TO : The Embryology of the Skeletal System
... ends; the epiphyses are still cartilaginous. A temporary a cartilage plate remains between the diaphyseal epiphyseal ossification centers. The epiphyseals plate plays an important role in growth and length of the bones of the embryo. When the bones has acquired its full length, the epiphyseal plates ...
... ends; the epiphyses are still cartilaginous. A temporary a cartilage plate remains between the diaphyseal epiphyseal ossification centers. The epiphyseals plate plays an important role in growth and length of the bones of the embryo. When the bones has acquired its full length, the epiphyseal plates ...
The evolution of developmental gene networks
... series of zygotic gap genes (i.e. giant, Krüppel, tailless), named so because their mutation leads to gaps in the region of the embryo in which they are normally expressed. The protein products of the gap genes themselves diffuse within the syncytial blastoderm, regulate each other and thus further ...
... series of zygotic gap genes (i.e. giant, Krüppel, tailless), named so because their mutation leads to gaps in the region of the embryo in which they are normally expressed. The protein products of the gap genes themselves diffuse within the syncytial blastoderm, regulate each other and thus further ...
ppt - Chair of Computational Biology
... V4 Full understanding of gene transcription: gene regulatory networks This lecture is fully based on ...
... V4 Full understanding of gene transcription: gene regulatory networks This lecture is fully based on ...
A gene complex controlling segmentation in Drosophila
... larval tracheal system, strongly transforms toward LMS in a double mutant combination involving bithorax-3 (bx 3 ) and postbithorax (pbx), notably producing a four-winged fll's, Substances S1 and S2 are assumed to be the products of bx+ and pbx+, respectively (Table 1), and to be involved in effecti ...
... larval tracheal system, strongly transforms toward LMS in a double mutant combination involving bithorax-3 (bx 3 ) and postbithorax (pbx), notably producing a four-winged fll's, Substances S1 and S2 are assumed to be the products of bx+ and pbx+, respectively (Table 1), and to be involved in effecti ...
Ch 21 C ppt - Houston ISD
... segment activates genes for antennal development. • A mutant version of this protein may label a segment as “thoracic” instead of “head”, causing legs to develop in place of antennae. ...
... segment activates genes for antennal development. • A mutant version of this protein may label a segment as “thoracic” instead of “head”, causing legs to develop in place of antennae. ...