* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download lecture24_RnaInterfe.. - University of Alberta
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Transposable element wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid tertiary structure wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
Short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
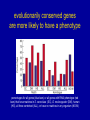
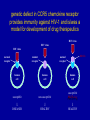
revisions to the “central dogma” of molecular biology genomic DNA mRNA1 no introns protein isoform1 mRNA2 no introns protein isoform2 pre-mRNA with introns non-coding RNA genes over the last 10 years, scientists have discovered an entirely new category of non-coding RNA genes whose existence had never even been suspected; they are distinguished by their small sizes relative to traditional RNA genes (i.e. 21 to 25 bp versus 96 bp) and are therefore commonly referred to as “microRNAs” The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2006 Andrew Z. Fire Stanford University School of Medicine b. 1959 Craig C. Mello University of Massachusetts Medical School b. 1960 for their discovery of RNA interference gene silencing by double-stranded RNA microRNA biogenesis and action gene silencing is mediated by short double-stranded RNAs (dsRNAs) microRNA-mediated gene silencing is observed in plants, animals, and many fungi; it plays essential roles in development and virus resistance; it has already provided powerful tools for studying gene function and spawned new therapeutic industries Saumet A, Lecellier CH. 2006. Retrovirology 3: 3 biologists working with transgenic plants had long observed a bewildering array of unanticipated gene silencing phenomena; in 1998, Fire and Mello compared the silencing activity of singlestranded RNAs (ssRNAs) (sense or antisense) with double-stranded (dsRNAs) hybrids; marginal silencing was achieved by injecting C. elegans with ssRNAs, but potent and specific silencing was achieved by injecting a sense-antisense mixture; in other words it is the dsRNAs that matter functional genomics of C. elegans chromosome 1 by RNA interference ingestion of bacteria expressing dsRNAs is as effective for gene silencing as the direct injection of dsRNAs C. elegans scientists can silence nearly any desired gene just by feeding the worm with one of these custommodified bacteria they sell on the Internet Fraser AG, …, Ahringer J. 2000. Nature 408: 325-330 (notice how few genes have an identifiable phenotype) evolutionarily conserved genes are more likely to have a phenotype percentages for all genes (blue bars) or all genes with RNAi phenotype (red bars) that have matches in S. cerevisiae (SC), D. melanogaster (DM), human (HS), all three combined (ALL), or have no matches in any organism (NO M) commercial libraries are widely available for most popular organisms RNA interference identifies over 250 host factors required by HIV-1 Brass AL, …, Elledge SJ. 2008. Science 319: 921-926 genetic defect in CCR5 chemokine receptor provides immunity against HIV-1 and is/was a model for development of drug therapeutics HIV virus HIV virus HIV virus normal receptor mutant receptor human cell DRUG normal receptor human cell human cell susceptible non-susceptible susceptible PLUS drug DISEASED HEALTHY HEALTHY RNAi exists because eukaryotic cells make microRNAs of their own Griffiths-Jones S, et al. 2008. Nucleic Acids Res 36: D154-D158 the miR-124 regulatory network gene batteries to global regulators of transcription and alternative splicing active interactions are solid black; inactive interactions are solid gray; weak interactions are thinner lines; gene battery expression inputs to cellular transcriptome are dashed lines; non-neuronal elements have dark blue coloring if present or light blue if absent; neuronal specific elements are likewise colored in shades of reds Makeyev EV, Maniatis T. 2008. Science 319: 1789-1790 Amaral PP, …, Mattick JS. 2008. The eukaryotic genome as an RNA machine. Science 319: 1787 how many other RNA mechanisms are remaining to be discovered?!?