* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Recombinant DNA Technologies
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified food wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
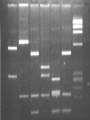
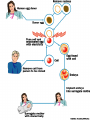
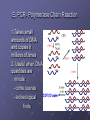
Recombinant DNA Technologies A.DNA- Deoxyribonucleic Acid 1. Bases: A- Adenine b. C- Cytosine c. G- Guanine d. T- Thymine -put together in a double-helical molecule with A-T & C-G as the “rungs” -form GENES e. We have about 30,000 genes and they are mapped by location on each chromosome -”Human Genome Project” f. We are 99.9% identical; .1% makes us unique and different from Rob Marder (thank heaven!) a. B. DNA fingerprinting 1. Find areas of variation 2. Hit with restriction enzymes =>neat DNA cutting tools (listen for where they came from!) 3. Run through a gel (electrophoresis) a. After cutting, small particles move fast, larger ones move slowly b. Gives a banding pattern: Gel Electrophoresis & Apparatus Two examples to try: -Crime Scene & Paternity Testing (Maury Povich style!) C. Gene Therapy 1. Problems with gene expression lead to faulty molecules, especially enzymes -cannot do their jobs 2. examples: Cystic Fibrosis & Tay Sachs diseases 3. Idea: replace bad genes with good ones that make the proper molecule And theoretically “fix” the problem 4. How can we deliver the new genes? (i.e. what do we know that inserts genes over existing ones…. Think “poison”) Called “vectors” D. Cloning 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Genetically identical copies Replace nucleus of egg w/ compat. Adult DIPLOID nucleus and jolt w/ electricity Age of clone- new or as old as donated DNA? Just because we can, does that mean we should? Examples: E. PCR- Polymerase Chain Reaction 1.Takes small amounts of DNA and copies it millions of times 2. Useful when DNA quantities are minute -crime scenes -archeological finds F. Transgenic organisms 1. Organisms with foreign DNA spliced into it 2. Examples: a. Bacteria- make chemicals that we need 1) insulin (rather than from a dead pig’s organ) 2) fertilizers 3) hormones 4) nutrasweet (phenylalanine- watch out PKU people) 5) Spider silk for manufacturing b. Plants 1) Resist frost (Arctic flounder gene) 2) Disease resistance Transgenic organisms continued: c. Animals 1. Goats that produce anticlotting protein 2. Glowing Rabbits: -Fun , but actually are “markers” 3. “Human” Mice Benefit? 4. Rejection –resistant pigs for organ transplants into humans (xenotransplantation) Example of how we generate HUMAN insulin from bacteria: •What are some benefits to utilizing this method? •How did Diabetics get their insulin before this was developed? •Hint: Our friend, the pig Genetic engineering funnies