* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download No Slide Title
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
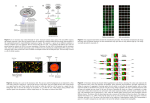
Gene Expression Biology 224 Instructor: Tom Peavy October 4 & 6, 2010 <Images from Bioinformatics and Functional Genomics by Jonathan Pevsner> Lecture Outline • cDNAs, ESTs and UniGene • Digital Differential Display • SAGE • Microarrays Gene expression is regulated in several basic ways • by region (e.g. brain versus kidney) • in development (e.g. fetal versus adult tissue) • in dynamic response to environmental signals (e.g. immediate-early response genes) • in disease states • by gene activity DNA RNA protein DNA cDNA RNA cDNA UniGene SAGE Microarray protein Analysis of gene expression in cDNA libraries A fundamental approach to studying gene expression is through cDNA libraries. • Isolate RNA (always from a specific organism, region, and time point) insert • Convert RNA to complementary DNA • Subclone into a vector • Sequence the cDNA inserts. These are expressed sequence tags (ESTs) vector Types of cDNA libraries • standard cDNA libraries in a vector that can be propagated • PCR-based cDNA libraries using PCR adaptors • normalized libraries (mRNA hybridized to cDNA-beads) •Subtraction libraries (mRNA from target is hybridized to cDNA-beads from other tissue) UniGene: unique genes via ESTs • www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/UniGene • UniGene clusters contain many ESTs • UniGene data come from many cDNA libraries. Thus, when you look up a gene in UniGene you get information on its abundance and its regional distribution. Cluster sizes in UniGene This is a gene with 1 EST associated; the cluster size is 1 Cluster sizes in UniGene This is a gene with 10 ESTs associated; the cluster size is 10 Cluster sizes in UniGene 1) Gene links are found for ESTs. 2) The set of mRNA sequences is compared with itself. 3) Sequence pairs that are sufficiently similar are linked together to form initial clusters. **Thus, this is a single cluster with a size of 10 (number of ESTs linked to site) This is a gene with 10 ESTs associated; the cluster size is 10 Cluster sizes in UniGene Cluster size Number of clusters 1 34,000 2 14,000 3-4 15,000 5-8 10,000 9-16 6,000 17-32 4,000 500-1000 500 2000-4000 50 8000-16,000 3 >16,000 1 Digital Differential Display (DDD) in UniGene • http:/www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/UniGene/ddd.cgi • Given that UniGene data come from many cDNA libraries and cluster contain many ESTs • Libraries can be compared electronically to look for expression differences UniGene brain libraries UniGene lung libraries CamKII up-regulated in brain n-sec1 up-regulated in brain surfactant upregulated in lung Pitfalls in interpreting cDNA library data • bias in library construction • variable depth of sequencing • library normalization • error rate in sequencing • contamination (chimeric sequences) Serial analysis of gene expression (SAGE) • 9 to 11 base “tags” correspond to genes • measure of gene expression in different biological samples • SAGE tags can be compared electronically • Longer SAGE tags can be produced and have greater specificity e.g. I-Sage™ Long from Invitrogen SAGE Library Construction & Analysis Microarrays: tools for gene expression A microarray is a solid support (such as a membrane or glass microscope slide) on which DNA of known sequence is deposited in a grid-like array. RNA is isolated from matched samples of interest. The RNA is typically converted to cDNA, labeled with fluorescence (or radioactivity), then hybridized to microarrays in order to measure the expression levels of thousands of genes. Advantages of microarray experiments Fast Data on 20-50,000 genes in days Comprehensive Entire genome represented on 1-2 chip(s) Flexible • Countless organisms available • Custom arrays can be made to represent genes of interest Easy You can submit RNA samples to a core facility for analysis Cheap? Chip set representing 47,000 genes for $350 Robotic spotter/scanner cost $100,000 In-house much cheaper, time consuming Observation Microarrays - Global Gene Expression Hypothesis Generation Generate hypotheses about the mechanisms underlying observed phenotypes (disease) Ability to uncover unanticipated connections What can you do with information about the expression of thousands of genes? Examples? •Breast cancer samples that have same tissue appearance but why different survival of patients? •Genes involved in biological processes •Genes involved in disease pathogenesis •Pathways for drug targets; Pathways targeted by drugs! Disadvantages of microarray experiments Many researchers can’t afford to do appropriate controls, replicates Cost RNA Do mRNA levels reflect Protein expression? significance Quality control* Cross hybridization Imperfections on arrays leading to error Difficulty of data analysis: statistics to evaluate In-house; repeatability by others? *this is less of an issue as the technology matures and becomes more common place: use of commercial arrays A microarray is a tool to rapidly evaluate gene expression (mRNA level) for tens of thousands of genes in a sample GeneChip is a brand microarray made by Affymetrix 1.3cm x 1.3cm Stage 1: Experimental design [1] Biological samples: technical vs biological replicates (technical- repetition of same samples; biological- use multiple biological sources) [2] RNA extraction, conversion, labeling, hybridization [3] Microarray platform (dual color or single color) X Pooling of samples and mRNA Single color (one sample on one microarray) Dual color (two samples on one microarray) Sample acquisition RNA: purify, label Data acquisition Microarray: hybridize, wash, image Data analysis Data confirmation (validation) Biological insight Stage 2: RNA and sample preparation For Affymetrix chips, need total RNA (about 2-10 ug) Confirm purity by running agarose gel Measure A260/A280 to confirm purity & quantity or use a Bioanalyzer (capillary electrophoresis) even better yet (can also determine quality) “Garbage in = Garbage out” RNA quality is key! Stage 3: hybridization to DNA arrays The array consists of cDNA or oligonucleotides Oligonucleotides can be deposited by photolithography The sample is converted to cRNA or cDNA ------------------Hybridization for hours or overnight… sample bind to complimentary sequences on microarray Stage 4: Image analysis mRNA expression levels are quantitated Fluorescence intensity is measured with a scanner, or radioactivity with a phosphorimager Control Sample #1 Test Sample #1 Stage 5: Microarray data analysis Hypothesis testing • How can arrays be compared? • Which RNA transcripts (genes) are regulated? • Are differences authentic? • What are the criteria for statistical significance? Clustering • Are there meaningful patterns in the data (e.g. groups)? Classification • Do RNA transcripts predict predefined groups, such as disease subtypes? Page 180 Microarray data analysis preprocessing global normalization local normalization scatter plots inferential statistics t-tests ANOVA Ratio exploratory statistics clustering Rattus norvegicus Ceruloplasmin (ferroxidase) (Cp), mRNA. ANOVA analysis, P = 0.00000566 RATIO ANALYSIS, fold change 4.3 upregulated in Diabetic Group 2000 1800 1600 Average Expression Intensity (n=5, biological replicates) 1400 1200 1000 800 600 400 200 0 Control Diabetic Quantified Gene Expression Differentially Expressed Genes (Based on p-value and fold change) Biological Interpretation Gene Ontology Literature Mining (Pubmatrix) Pathways (KEGG) BLAST ESTs Clustering grouping Identifying Genes Selectively Expressed in a group Two-dimensional hierarchical clustering using complete link and Pearson correlation using only those genes with comparison p-value 0.01 between at least two groups. Stage 6: Confirmation and Validation The differential up- or down-regulation of specific genes can be measured using independent assays such as -- Northern blots (not done much anymore) -- Polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) -- In situ hybridization --Western blot --Immunohistochemistry Stage 7: Microarray databases There are two main repositories: Gene expression omnibus (GEO) at NCBI ArrayExpress at the European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI) Array Express at the European Bioinformatics Institute http://www.ebi.ac.uk/arrayexpress/