* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DYNC2H1 Clipson Family Variants 27.11.09 1.I2526S/N c.7577T>G
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Transposable element wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Whole genome sequencing wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Human Genome Project wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
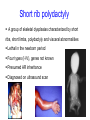
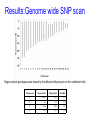
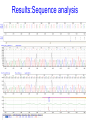
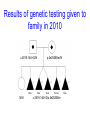
Genome wide SNP analysis leads to the identification of compound heterozygous mutations in a pedigree with multiple pregnancies affected with short rib polydactyly type III Sian Ellard1, Ann-Marie Patch1, Elizabeth Young1, Anna L. Gloyn3 and Peter D. Turnpenny2 Departments of Molecular Genetics1 and Clinical Genetics2, Royal Devon & Exeter NHS Foundation Trust and Oxford Centre for Diabetes3, Endocrinology and Metabolism, Churchill Hospital Family referred to Peninsula Clinical Genetics service in 2000 Born 1996 TOP 20/40 1999 Short rib polydactyly A group of skeletal dysplasias characterized by short ribs, short limbs, polydactyly and visceral abnormalities Lethal in the newborn period Four types (I-IV), genes not known Presumed AR inheritance Diagnosed on ultrasound scan Family referred to Peninsula Clinical Genetics service in 2000 Born 1996 TOP15-20 weeks’ gestation between 1999 and 2003 Aim To identify the causative gene mutation(s) in the affected foetuses Methods DNA extracted from paraffin-embedded fixed tissue stored from the 5 affected foetuses, their unaffected sibling and both parents Genome wide linkage analysis (Illumina Golden Gate n=6008 SNPs) Fine mapping using microsatellite markers Sequence analysis of candidate gene Results:Genome wide SNP scan Genotype call rate 98.9% for FFPE DNA vs 99.7% for lymphocyte DNA No homozygous regions exceeding 3cM Perl script written to identify informative markers where affected offspring share a genotype but the unaffected child does not Results:Genome wide SNP scan Results:Genome wide SNP scan Regions where genotypes were shared by the affected offspring but not the unaffected child. Chromosome Physical Start Physical End Size (Mb) 5 166.1 172.3 6.2 6 2.2 3.7 1.5 11 97.6 107.3 9.8 17 24.9 28.1 3.2 Results:Microsatellite analysis 16 microsatellites tested Chromosome Physical Start Physical End Size (Mb) 5 166.1 172.3 6.2 6 2.2 3.7 1.5 11 97.6 103.6 6.0 17 24.9 28.1 3.2 Results:Candidate genes 6Mb containing 21 genes Chromosome 11 Results:DYNC2H1 candidate gene DYNC2H1 encodes a dynein motor protein required for generation and maintenance of cilia Jeune asphyxiating thoracic dystrophy is a skeletal dysplasia caused by mutations in the IFT80 gene that encodes a protein involved in intraflagellar transport of primary cilia (Beales et al 2007 Nature Genetics) Where next? Sequence best functional candidate (DYNC2H1, 90 exons) or Array capture of 6Mb region for next generation sequencing Results:Sequence analysis Results:Sequence analysis Results:Splicing prediction p.Ala940ValfsX8 Results of genetic testing given to family in 2010 c.2819-14A>G/N N/N p.Ile2526Ser/N c.2819-14A>G/p.Ile2526Ser Conclusions DYNC2H1 mutations confirmed in a 9th family with short rib polydactyly type III First example of linkage mapping to identify compound heterozygous mutations in an outbred family affected with a recessive disorder Ten years from referral to report; how long using next generation sequencing technology? Acknowledgements The family Helen Butler and Cecilia Lindgren, Wellcome Trust Centre, Oxford Nathalie Dagoneau and Valerie Cormier-Daire, Paris Karen Stals, Exeter Northcott Devon Medical Foundation