* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ppt
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Segmental Duplication on the Human Y Chromosome wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Transposable element wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
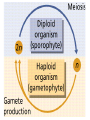
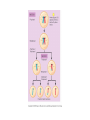
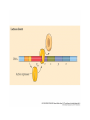
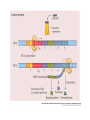
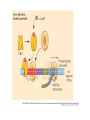
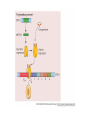
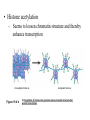
Heredity Review Asexual reproduction Hydra (related to jelly-fish Single celled eukaryotes like this protist Zygote (2n) - diploid n chromosomes Independent Assortment Codominance Incomplete Dominance Epistasis Thomas Hunt Morgan Discovered sex-linked traits • The recessive mutations s (scute bristles) and rb (ruby eyes) identify two linked autosomal genes of Drosophila melanogaster. When females heterozygous for these genes were crossed with scute bristled, ruby eyed males, the following classes and numbers of progeny (out of 1000) were obtained: • wildtype bristles, wildtype eyes 188 • scute bristles, wildtype eyes 307 • wildtype bristles, ruby eyes 313 • scute bristles, ruby eyes 192 Based upon these results, the map distance between the s and rb genes is estimated to be: • A. 31.3 map units • B. 38 map units • C. 30.7 map units • D. greater than 50 units because all four classes of offspring were observed DNA (pattern done by Rosalind Franklin, Model completed by Watson and Crick) Promoter includes the TATA box; has the core DNA sequence 5'-TATAAA-3' or a variant, which is usually followed by three or more adenine bases. It is usually located 25 base pairs upstream to the transcription site. The sequence is believed to have remained consistent throughout much of the evolutionary process, possibly originating in an ancient eukaryotic organism. G 5” cap and Poly A tail and reomval of introns Conjugation • Histone acetylation – Seems to loosen chromatin structure and thereby enhance transcription Unacetylated histones Figure 19.4 b Acetylated histones (b) Acetylation of histone tails promotes loose chromatin structure that permits transcription Evolution of Genes with Related Functions: The Human Globin Genes • The genes encoding the various globin proteins – Evolved from one common ancestral globin gene, which duplicated and diverged Ancestral globin gene Duplication of ancestral gene Mutation in both copies Transposition to different chromosomes Further duplications and mutations Figure 19.19 2 2 1 1 -Globin gene family on chromosome 16 G A -Globin gene family on chromosome 11 • The similarity in the amino acid sequences of the various globin proteins – Supports this model of gene duplication and mutation • Subsequent duplications of these genes and random mutations – Gave rise to the present globin genes, all of which code for oxygen-binding proteins Genomic library Bands form due to SNP’s -Single nucleotide polymorphisms A single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP, pronounced snip), is a DNA sequence variation occurring when a single nucleotide - A, T, C, or G - in the genome (or other shared sequence) differs between members of a species (or between paired chromosomes in an individual). For example, two sequenced DNA fragments from different individuals, AAGCCTA to AAGCTTA, contain a difference in a single nucleotide. In this case we say that there are two alleles : C and T