* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Living World
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Protein phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Protein folding wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
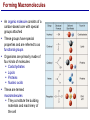
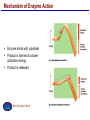
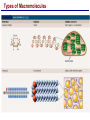
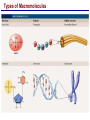
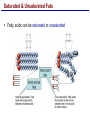
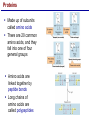
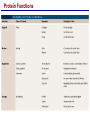
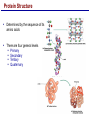
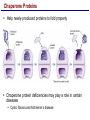
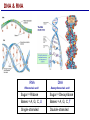
Lecture 3 Macromolecules Forming Macromolecules An organic molecule consists of a carbon-based core with special groups attached These groups have special properties and are referred to as functional groups Organisms are primarily made of four kinds of molecules Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic acids These are termed macromolecules They constitute the building materials and machinery of the cell Macromolecule Formation & Breakdown Macromolecules are made by a process termed dehydration synthesis Macromolecules are broken down by a process termed hydrolysis Both types of processes require enzymes Mechanism of Enzyme Action Enzyme binds with substrate Product is formed at a lower activation energy Product is released PLAY How Enzymes Work Types of Macromolecules Types of Macromolecules Carbohydrates Also referred to as sugars Provide building materials and energy storage Are molecules that contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio Are of two main types: Simple carbohydrates Complex carbohydrates Simple Carbohydrates Monosaccharides Consist of one subunit Disaccharides Consist of two subunits Complex Carbohydrates Consist of long polymers of sugar subunits Also termed polysaccharides Examples: Starch provides energy storage in plants Glycogen provides energy storage in animals Cellulose is found in the cell walls of plants Chitin is found in the cell walls of fungi & insect exoskeletons Carbohydrate Functions Carbohydrate Functions Three Forms of Lipids Large nonpolar molecules that are insoluble in water Fats Used for long-term energy storage Also termed triglycerides or triacylglycerol Composed of three fatty acid chains linked to glycerol Phospholipids A modified fat One of the three fatty acids is replaced by a phosphate and a small polar functional group In water, phospholipids aggregate to form a lipid bilayer Steroids Composed of four carbon rings Examples: Cholesterol Found in most animal cell membranes Male and female sex hormones Saturated & Unsaturated Fats Fatty acids can be saturated or unsaturated Proteins Made up of subunits called amino acids There are 20 common amino acids, and they fall into one of four general groups Amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds Long chains of amino acids are called polypeptides Protein Functions Protein Functions Protein Structure Determined by the sequence of its amino acids There are four general levels Primary Secondary Tertiary Quaternary Protein Structure Primary structure The specific amino acid sequence of a protein Secondary structure The initial folding of the amino acid chain by hydrogen bonding PLAY Chemistry of Life: Proteins: Secondary Structure Tertiary structure The final three-dimensional shape of the protein PLAY Chemistry of Life: Proteins: Tertiary Structure Quaternary structure The spatial arrangement of polypeptides in a multi-component protein PLAY Chemistry of Life: Proteins: Quaternary Structure Protein Structure Proteins can be divided into two classes 1. Structural Long cables Provide shape/strength 2. Globular Grooves and depressions Enzymes Changes in a protein’s environment can cause a protein to denature It loses its three-dimensional structure and becomes inactive Chaperone Proteins Help newly-produced proteins to fold properly Chaperone protein deficiencies may play a role in certain diseases Cystic fibrosis and Alzheimer’s disease Nucleic Acids Serve as information storage molecules Long polymers of repeating subunits termed nucleotides A nucleotide is composed of three parts Five-carbon sugar Nitrogen-containing base Phosphate DNA & RNA RNA Ribonucleic acid DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid Sugar = Ribose Bases = A, G, C, U Sugar = Deoxyribose Single-stranded Double-stranded Bases = A, G, C, T