* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download From Genes to Proteins
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
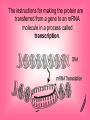
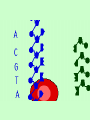
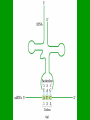
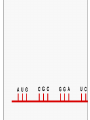
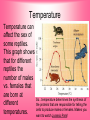
From Genes to Proteins All About RNA Quick Review • The building blocks of proteins are amino acids. • They have many different functions. They can be enzymes, hormones, or any of a number of substances your body needs. • Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis. • RNA is made of nucleotides. – A phosphate group – Ribose – Nitrogen base • RNA is a single strand. • RNA uses uracil instead of thymine. • Three types: – mRNA – messenger RNA – tRNA – transfer RNA – rRNA – ribosomal RNA The instructions for making a protein are encoded in the genes in the DNA. The instructions for making the protein are transferred from a gene to an mRNA molecule in a process called transcription. • Cells then use tRNA and rRNA to read the instructions on the mRNA molecule and put together the amino acids that make up the protein in a process called translation. Transcription • Takes place in the nucleus. • Starts at a ‘start’ signal and ends with a ‘stop’ signal. • Requires RNA polymerase – Opens DNA – Adds complementary nucleotides of RNA •mRNA then leaves through the nuclear pores out to the cytoplasm where it settles on a ribosome. Genetic Code • The instructions for making proteins are written as a series of three-nucleotide sequences on the mRNA called codons. • Each codon codes for an amino acid or signals a start or stop for translation. • AUG = start • UAG = stop UAG (STOP) • Do the Quick Lab on page 210… Translation • Takes place in the cytoplasm on the ribosomes. • tRNA molecules are single strands of RNA that temporarily carry an amino acid on one end. • Each tRNA contains an anticodon for the mRNA’s codon. • The anticodon is a three-nucleotide sequence that is complementary to a particular mRNA codon. Translation continues… • When a tRNA’s anticodon matches up with the codon of mRNA, it drops off its’ amino acid. • Each amino acid forms a peptide bond with the previous amino acid which results in the production of a protein. DATA LAB Keratin is one of the proteins in hair. The gene for keratin is transcribed and translated by certain skin cells. The series of letters on the next slide represents the sequence of nucleotides in a portion of an mRNA molecule transcribed from the gene for keratin. This mRNA strand and the genetic code on page 211 can be used to determine some of the amino acids in keratin. UCUCGUGAAUUUUCC 1. Determine the sequence of amino acids that will result from the translation of the segment of mRNA above. (Use chart on p. 211.) 2. Determine the anticodon of each tRNA molecule that will bind to this mRNA segment. 3. Determine the sequence of nucleotides in the segment of DNA from which the mRNA strand above was transcribed. 4. Determine the sequence of nucleotides in the segment of DNA that is complementary to the DNA segment described in item 3. Environmental Factors and Protein Synthesis The development of a growing zygote (fertilized egg) is controlled by different types of proteins produced by that cell. Certain factors can inhibit, enhance, or change the way those proteins work. http://www.idreamofzygotes.com/.a/6a01287709b095970c0128 77135951970c-800wi For instance… Temperature Temperature can affect the sex of some reptiles. This graph shows that for different reptiles the number of males vs. females that are born at different temperatures. So…temperature determines the synthesis of the proteins that are responsible for telling the cells to produce males or females. Makes you want to watch Jurassic Park! Water Some species of animals, including frogs and insects that lay eggs in ponds that evaporate quickly, have developed an adaptation that allows metamorphosis to occur more quickly. So…the availability of water determines the synthesis of the proteins that are responsible for telling the cells to develop more quickly. Frogs: yea! Mosquitoes? Not so much… Nutrients Lack of certain proteins, fats, carbohydrates, minerals, or vitamins can cause cells to produce incorrect proteins or to not produce certain proteins, at all. This can lead to many So…the availability of nutrients determines disorders. which proteins are synthesized. Salad, anyone? Just checking! 1. How many types of RNA are there and what are they? 2. What are the two steps to protein synthesis? 3. Discuss how protein synthesis is necessary to development in all organisms, no matter how small.