* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology Ch 10 How Proteins are Made
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
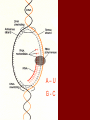
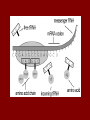
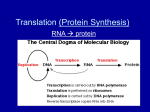
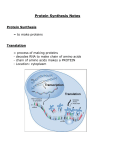
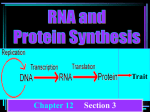
Biology Ch 10 How Proteins are Made Section 1 From Genes to Protein Importance of Proteins • You are who you are based on your ability to make specific proteins • Many diseases are caused by the bodies inability to make specific proteins properly – – – – Diabetes Cystic Fibrosis Sickle Cell Anemia Albinism • The information on how to make those proteins is stored in the genes (DNA) From Genes to Proteins • The genes don’t directly make proteins – A combined effort between 3 types of RNA • RNA = ribonucleic acid – Long chain of nucleotides – 4 N bases include adenine, guanine, cytosine, and URACIL – A-U G-C Gene Expression 1. Transcription • • DNA used as a template to form mRNA mRNA can leave the nucleus 2. Translation • • mRNA message used to create a polymer of amino acids = protein tRNA and rRNA work together to deliver the proper amino acids in the proper order Transcription • DNA is unwound and unzipped at the site of the gene to be expressed (promoter) • RNA polymerase adds the complementary nucleotides to the exposed DNA nucleotides – Every three mRNA bases is called a codon • Process ends when a stop signal is reached. A single strand of mRNA can then leave the nucleus and enter the cytoplasm (ribosome) A–U G-C Translation • Takes place in the cytoplasm (ribosome) – rRNA • Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules deliver the proper amino acids to the ribosome • Each codon codes for a specific amino acid • tRNA molecules have an anti-codon that matches the codon • The delivered AA attaches to the chain adding to the polymer (protein) Amino Acid Chart for mRNA