* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Expression vector wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Real-time polymerase chain reaction wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
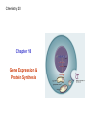
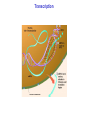
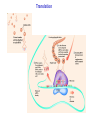
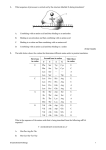
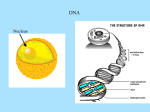
Chemistry 20 Chapter 18 Gene Expression & Protein Synthesis Functions of DNA 1. It reproduces itself (Replication) Chapter 17 2. It supplied the information to make up RNA, proteins, and enzymes. Central dogma Central dogma of molecular biology: Information contained in DNA molecules is expressed (encoded) to the production of proteins. Gene expression: activation of a gene to produce a specific protein. Gene expression Transcription: synthesis of mRNA (messenger RNA) Translation DNA replication RNA replication DNA Transcription mRNA Reverse transcription Revers e transcriptase Translation protein Transcription Genetic information is copied from a gene in DNA to make a mRNA. Begins when the section of a DNA that contains the gene to be copied unwinds. Polymerase enzyme identifies a starting point to begin mRNA synthesis. Transcription C is paired with G, T pairs with A But A pairs with U (not T). Polymerase enzyme moves along the unwound DNA, forming bonds between the bases. RNA Polymerase Section of bases on DNA: Complementary base sequence in mRNA: -G–A–A–C–T-C–U–U–G–A- Translation mRNA (as a carrier molecule) moves out of the nucleus and goes to ribosomes. tRNA converts the information into amino acids. Amino acids are placed in the proper sequence. Proteins are synthesized. Gene expression Overall function of RAN’s in the cell: facilitate the task of synthesizing protein. Genetic code Genetic code: language that relates the series of nucletides in mRNA to the amino acids specified. • The sequence of nucleotides in the mRNA determines the amino acid order for the protein. • Every three bases (triplet) along the mRNA makes up a codon. • Each codon specifies a particular amino acid. • Codons are present for all 20 amino acids. Genetic code 5' U C U UUU UUC UUA UUG CUU CUC CUA CUG AU U AU C A AU A AU G GU U G GU C GU A GU G Phe Phe Leu Leu Leu Leu Leu Leu Ile Ile Ile Met* Val Val Val Val C UCU UCC UCA UCG Ser Ser Ser Ser A U AU U AC U AA U AG CAU CAC CAA CAG Tyr Tyr Stop Stop His His Gln Gln G U GU U GC U GA U GG CGU CGC CGA CGG Cys Cys S top Trp Arg Arg Arg Arg CCU CCC CCA CCG Pro Pro Pro Pro ACU ACC ACA ACG GCU GCC GCA GCG Thr Thr Thr Thr Ala Ala Ala Ala AAU AAC AAA AAG GAU GAC GAA GAG As n As n Lys Lys A sp A sp Glu Glu A GU A GC A GA A GG GGU GGC GGA GGG Ser Ser Arg Arg Gly Gly Gly Gly 3' U C A G U C A G U C A G U C A G *AUG s ign als tran slation initiation as w ell as codin g for Met Genetic code • 64 condons are possible from the triplet combination of A, G, C, and U. • UGA, UAA, and UAG, are stop signals. (code for termination of protein synthesis). • AUG has two roles: 1. Signals the start of the proteins synthesis (at the beginning of an mRNA). 2. Specifies the amino acid methionine (Met) (in the middle of an mRNA). tRNA (transfer RNA) tRNA translates the codons into specific amino acids. Serine Anticodon loop A G U Codon on mRNA U C A Transcription Translation Protein synthesis • mRNA attaches to smaller subunit of a ribosome. • tRNA molecules bring amino acids to the mRNA. • Peptide bonds form between an amino acid and the end of the growing peptide chain. • The ribosome moves along mRNA until the end of the codon (translocation). • The polypeptide chain is released from the ribosome and becomes an active protein. Sometimes several ribosomes (polysome) translate the same strand of mRNA at the same time to produce several peptide chains. Termination 5' U C A G 3' C A G 3' UCU Ser U GU Cys UUU Phe U AU Tyr U Ribosome encounters a stop condon. UCU Ser Phe U AU UCCCys Ser U U AC Tyr U GC Cys UUCTyr Phe U GU C UCC Ser U GC Phe UCACys Ser C U AA Stop UUATyr Leu U U AC U GA S top A UCA Ser U AA Stop Leu Ser A U AG Stop UCGS top UUG Leu U GA U GG Trp G UCG Ser U AG Stop Leu U GG Trp G CUU Leu CCU Pro CAU His CGU Arg U His Leu CCU Pro CAU CUC Leu CGU CCCArg Pro U CAC His CGC Arg C No tRNA to complement the termination codon. HisLeu CGC Leu CCC Pro C CAC CUA CCAArg Pro C CAA Gln CGA Arg A GlnLeu CGA Leu CCA Pro CAA CUG CCGArg Pro A CAG Gln CGG Arg G Leu CCG Pro CAG Gln CGG Arg G AU U Ile AAU As n U ACU Thr A GU Ser An enzyme releases the complete polypeptide chain from the ribosome. AsIle n Ile AAU Ser U AAC As n ACU Thr A GU C AU C ACC Thr A GC Ser A AsIle n Ile ACC Thr AAC A GC A AU A ACASer Thr C AAA Lys A GA Arg Ile ACA Thr AAA LysMet*A GA Arg G AU G ACG Thr A AAG Lys A GG Arg G Met* ACG Thr AAG Lys A GG Arg GU U Val GCU Ala GAU A sp GGU Gly U Val GCU Ala GAU A sp GGU Gly Val Ala Ustructure sp Gly GU C GCC GAC A(active GGC C Amino acids form the three-dimensional protein). G Val Ala A sp Gly GCC GAC GU A Val GGC GCA Ala C GAA Glu GGA Gly A Val GCA Ala GluVal GGA Gly GAA GU G GCG Ala A GAG Glu GGG Gly G Val GCG Ala GGG Gly G GAG Glu *AUG s ign als tran slation initiation as w ell as codin g for Met ign als tran slation initiation as w ell as codin g for Met Mutation A heritable change in DNA nucleotide sequence. It changes the sequence of amino acids (structure and function of proteins). Enzyme cannot catalyze. X rays, Overexpose to sun (UV light), Chemicals (mutagens), or Viruses Effect of Mutation Somatic cell (nonreproductive cell): Altered DNA will be limited to that cell and its daughter cells. Cancer Germ cell (reproductive cell like egg or sperm): All new DNA will contain the same default. Genetic diseases Type of Mutations Substitution Mutation Most common Replacement of one base in the coding strand of DNA with another. Different amino acid Frameshift Mutation A base is added to or deleted from the normal order of bases in DNA. All the triplets shift over by one base. Different sequence of amino acids