* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lesson6.5_Translation Process
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Catalytic triad wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
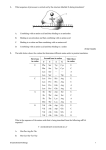
Monday, April 2, 2012 Homework: - Translation Checkup tomorrow - Translation Practice due tomorrow - Word Wall due on Block Day - Quiz on DNAProtein- Block Day Turn to entry from Friday: Translation (mRNAProtein)- turn to back of the worksheet (SIDE TWO) Watch the animation and fill in the steps on the worksheet. Make a new entry: Entry 31: Translation Notes- 4/2/12 See attached A D E C B 4 Components used in Translation 1. mRNA- the message to be translated into protein. 2. Amino acids- the building blocks that are linked together to form the protein. 3. Ribosomes- the “machines” that carry out translation. 4. tRNA (transfer RNA)- brings an amino acid to the mRNA and ribosome. -One end of a tRNA molecule has a 3 letter code that matches with an mRNA codon. - The other end has a specific amino acid. - A tRNA molecule with a particular 3 letter always carries the same type of amino acid. How does translation occur? How does translation occur? 1. The ribosome attaches to the mRNA molecule. 2. The tRNA attaches to the mRNA. The tRNA anticodon attaches to the mRNA codon. 3. The first two amino acids are joined/connected and the first tRNA leaves, and the ribosome moves along the mRNA to the next codon 4. The next tRNA brings in the next amino acid, adding to the growing amino acid chain. 5. The process continues with the ribosome moving along the mRNA and the amino acids linking together until a STOP codon is reached. 6. The chain of amino acids folds into a working protein—based on the attraction of the side chains. The CODE of translation mRNA nucleotides are translated in groups of 3 called codons. AUGCACUGCAGUCGAUGA CODONS U U C A G C A G UUU Phenylalanine (Phe) UCU Serine (Ser) UAU Tyrosine (Tyr) UGU Cysteine (Cys) U UUC Phe UCC Ser UAC Tyr UGC Cys C UUA Leucine (Leu) UCA Ser UAA STOP UGA STOP A UUG Leu UCG Ser UAG STOP UGG Tryptophan (Trp) G CUU Leucine (Leu) CCU Proline (Pro) CAU Histidine (His) CGU Arginine (Arg) U CUC Leu CCC Pro CAC His CGC Arg C CUA Leu CCA Pro CAA Glutamine (Gln) CGA Arg A CUG Leu CCG Pro CAG Gln CGG Arg G AUU Isoleucine (Ile) ACU Threonine (Thr) AAU Asparagine (Asn) AGU Serine (Ser) U AUC Ile ACC Thr AAC Asn AGC Ser C AUA Ile ACA Thr AAA Lysine (Lys) AGA Arginine (Arg) A AUG Methionine (Met) or START ACG Thr AAG Lys AGG Arg G GUU Valine Val GCU Alanine (Ala) GAU Aspartic acid (Asp) GGU Glycine (Gly) U GUC (Val) GCC Ala GAC Asp GGC Gly C GUA Val GCA Ala GAA Glutamic acid (Glu) GGA Gly A GUG Val GCG Ala GAG Glu GGG Gly G Each codon codes for a specific amino acid. 20 different amino acids can be used in different combinations to form a protein. For example: mRNA codon amino acid AAU asparagine CGC arginine GGG glycine - Amino Acid order determines shape. - Interactions between amino acids side chains folds of the chain. How is the amino acid sequence determined? • The mRNA • Each codon is a code for one amino acid DNA sequence: mRNA sequence: amino acid sequence: TACCGAGATTCA AUGGCUCUAAGU Met -- Ala -- Leu -- Ser Make an entry: Entry 32: Translation Practice-4/2/12 Met Pro U A CG G A