* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The control of complexity in the human genome
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Real-time polymerase chain reaction wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Transformation (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
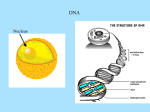
Exciting Developments in Molecular Biology As seen by an amateur Dr. Ray Sepeta 631-7421 [email protected] DNA sequences of nucleotides • • • • • • • • A – Adenine C – Cytosine G – Guanine T – Thymine N – any nucleotide base R – A or G Y – C or T - none (gap) RNA • • • • A – Adenine C – Cytosine G – Guanine U - Uracil Central Dogma DNA RNA transcription Protein translation Proteins strings of amino acids • • • • • • • • • • • G – Glycine – Gly A - Alanine – Ala L – Leucine – Leu M – Methionine – Met F - Phenylalanine-Phe W – Tryptophan – Trp K – Lysine – Lys S – Serine – Ser N – Asparagine – Asn D – Aspartic acid – Asp B – Aspartate - Asx • • • • • • • • • • • P – Proline – pro V – Valine – Val I – Isoleucine – Ile C – Cysteine – Cys Y – Tyrosine – Tyr H – Histidine – His R – Arginine – Arg T – Threonine – Thr Q – Glutamine – Gln E – Glutamic acid – Glu Z – Glutamate - Glx 5’ Base U U phe phe leu leu Genetic Code Middle Base C A ser tyr ser tyr ser quit ser quit G cys cys quit trp 3’ Base U C A G C leu leu leu leu pro pro pro pro his his gln gln arg arg arg arg U C A G A ile ile ile met thr thr thr thr asn asn lys lys ser ser arg arg U C A G G val val val val ala ala ala ala asp asp glu glu gly gly gly gly U C A G gene chromosome DNA base pairs RNA Watson and Crick Avery Hershey and Chase proteins amino acids genetic code codon central dogma sequence of DNA that codes for a protein contiguous stretch of DNA, contains many genes double helix of base pairs A, C, T, G A – T, G - C ribosomal, messenger, transfer (U for T) discovered structure DNA discovered transforming principle of DNA blender experiment sequence of amino acids, selected by codons and tRNA for proteins codon => amino acid three base pairs-together see slide virus bacteria prokaryote eukaryote nucleus cytoplasm exons introns number of genes c.elegans corn insects humans DNA (or RNA) in protein coat cell-metabolizes food to function cell without nucleus cell with a nucleus where mRNA is transcribed from DNA outside nucleus, proteins formed stretches of DNA converted to genes DNA excised, “junk” DNA 19,000 40,000 13,500 27,000 In prokaryotes there is no nucleus so transcription and translation occur almost simultaneously. So there is no time to splice out RNA segments Among eukaryotes as their complexity increases generally so too does the proportion of their junk DNA that does not code for protein Arguably the most important advance in biology in decades has been the discovery that RNA molecules can regulate the expression of genes. - Sharp The failure to recognize the importance of introns may well go down as one of the biggest mistakes in the history of molecular biology Less than 1.5 % of the human genome encodes for protein. Either the human genome (and that of other complex organisms) is replete with useless transcription, or these nonprotein-coding RNAs fulfill some unexpected function Generating complexity is easy, controlling it is not. Sources • • • • • Censors of the Genome, Sci. Am, Aug 03 Unseen Genome, Sci. Am, Nov 03 RNAi Revolution, Nature, Jul 04 Hidden Genetic Program, Sci. Am, Oct 04 Alternate Genome, Sci. Am, Apr 05