* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Brain Damage & Neuroplasticity
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Impact of health on intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
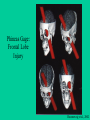
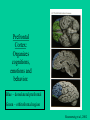
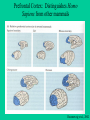
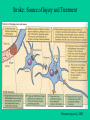
Brain Damage & Neuroplasticity Etiology of Brain Damage • • • • • • • Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Cerebrovascular Injury (CVI) Tumors Anoxia (e.g., near drowning, drug overdose) Toxins (e.g., lead) Diseases (e.g., Herpes, encephalitis) Seizures Traumatic Brain Injury 1. Open Head Injury (e.g., missile wound) – focal damage and some diffuse damage Classic Case: Phineas Gage Phineas Gage: Frontal Lobe Injury Rosenzweig et al., 2002 Prefrontal Cortex: Organizes cognitions, emotions and behavior. Blue – dorsolateral prefrontal Green – orbitofrontal region Rosenzweig et al., 2002 Prefrontal Cortex: Distinguishes Homo Sapiens from other mammals Rosenzweig et al., 2002 Behavioral Disruption Following Prefrontal Lesions (note: any type of brain damage can result in a Prefrontal Syndrome) Rosenzweig et al., 2002 Traumatic Brain Injury (cont’d) 2. Closed Head Injury - concussion (mild brain injury) - moderate to severe brain injury: classification dependent on the degree of post-traumatic amnesia (or anterograde amnesia – deficits in new learning) - Pathophysiology of TBI ~ focal damage (coupe & contra-coupe) ~ diffuse damage (shearing & tearing of axons referred to as diffuse axonal injury) Functional Changes: • Depends on where the focal damage is: – – – – – – – – Frontal? Parietal? Occipital? Temporal? Limbic System? Basal Ganglia? Hypothalamus? Brainstem? Identify behaviors associated with these areas. Focal damage can affect specific behaviors and impact related behaviors. Diffuse damage will cause widespread tissue loss. Cerebrovascular Injury • Stroke (Ischemia – loss or reduction of blood circulation) Thrombosis (large blockage) Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA) What causes the brain damage? (next slide) Stroke: Source of Injury and Treatment Rosenzweig et al., 2002 Behavioral Disruption following Right Hemisphere Stroke: Hemispatial Neglect Rosenzweig et al., 2002 Other Causes of Brain Damage: • Tumors – these can be small to large cyst-like tumors or sticky, tentacle-like tumors • Toxins – heavy metals such as lead cause damage. Lead replaces the oxygen molecule, causing widespread damage (sources: lead paint, leaded gasoline fumes) • Anoxia – loss of oxygen causes diffuse damage • Diseases – numerous… • Seizures – uncontrolled electrical activity cause Glutamate Toxic Casacade (as occurs with stroke) Did you know that… • if you understand the functional organization of the brain in a healthy person, you will be able to understand functional changes following brain damage? AND (if you understand this) • you will be able to understand problems associated with psychiatric disorders? Remember – There is always recovery due to Neuroplasticity Rosenzweig et al., 2002