* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Interphase - Cloudfront.net
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
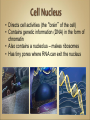
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
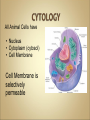
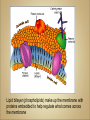
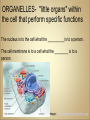
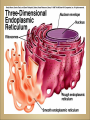
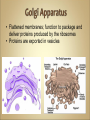
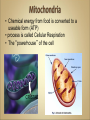
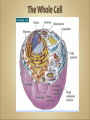
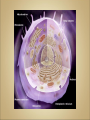
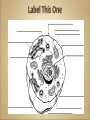
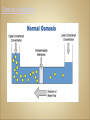
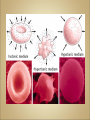
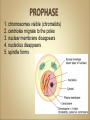
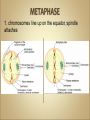
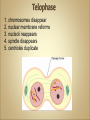
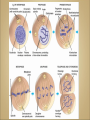
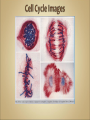
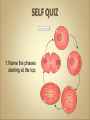
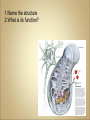
Cells Anatomy & Physiology Cells vary in SIZE and STRUCTURE Depends on what they do All Animal Cells have • Nucleus • Cytoplasm (cytosol) • Cell Membrane Cell Membrane is selectively permeable Lipid bilayer (phospholipids) make up the membrane with proteins embedded to help regulate what comes across the membrane ORGANELLES- "little organs" within the cell that perform specific functions The nucleus is to the cell what the __________is to a person. The cell membrane is to a cell what the ________ is to a person. Image: http://www.chemistrypictures.org • Transport system; canals and channels that connect membrane to nucleus and to organelles within the cell • Smooth ER (lipid synthesis) • Rough ER (contains ribosomes for protein manufacture) • Flattened membranes; function to package and deliver proteins produced by the ribosomes • Proteins are exported in vesicles • Chemical energy from food is converted to a useable form (ATP) • process is called Cellular Respiration • The “powerhouse” of the cell CRISTAE • Lysosomes - contain digestive enzymes to break down substances • Centrosome – forms a spindle during cell division • Vesicles – packaged substances, exported • Microfilaments and Microtubules - cell skeleton (cytoskeleton), maintains shape and functions in movement • Cilia & Flagella - movement • Directs cell activities (the “brain” of the cell) • Contains genetic information (DNA) in the form of chromatin • Also contains a nucleolus – makes ribosomes • Has tiny pores where RNA can exit the nucleus • Diffusion - molecules tend to spread out • Facilitated Diffusion Diffusion Animation o Hypertonic o Hypotonic o Isotonic SALT SUCKS Osmosis Animation Active Transport Exocytosis Endocytosis (phagocytosis & pinocytosis) • Mitosis = nuclear division • Mitosis is followed by cytokinesis (cell division) • The steps of mitosis ensure that each new cell has the exact same number of chromosomes as the original • Interphase = growth phase, differentiation occurs • Interphase • Prophase • Metaphase • Anaphase • Telophase •IPMAT 1. chromosomes visible (chromatids) 2. centrioles migrate to the poles 3. nuclear membrane disappears 4. nucleolus disappears 5. spindle forms 1. chromosomes line up on the equator, spindle attaches 1. chromatids separate and move to opposite poles 1. chromosomes disappear 2. nuclear membrane reforms 3. nucleoli reappears 4. spindle disappears 5. centrioles duplicate - division of the cytoplasm to form 2 new daughter cells - organelles are divided - daughter cells are genetically identical Cells return to interphase 1.Name the phases starting at the top. 1.Name the phase 2.Identify X 3.Identify Y 5. Name the phase 6. Name the structure 1.Name the structure 2.What is its function? 9. Which beaker(S) contains a solution that is hypertonic relative to the bag A B C D E 10. What will happen to the baggie in the hypertonic solutions?






















![MITOSIS WORKSHEET - New Page 1 [bs079.k12.sd.us]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014668413_1-30813973b0cb9de17ced950a5cb16263-150x150.png)




