* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells - Mrs. GM Biology 200
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
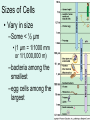
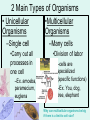
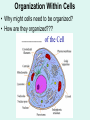
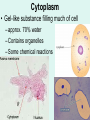
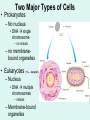
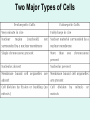
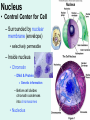
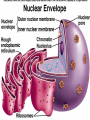
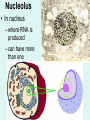
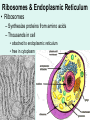
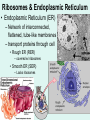
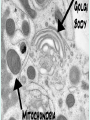
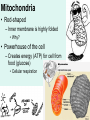
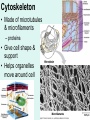
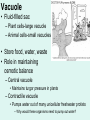
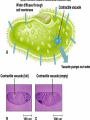
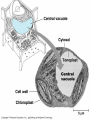
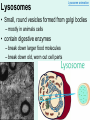
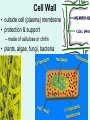
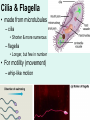
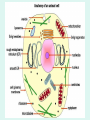
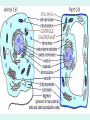
Unit 3: The Cell & Its Environment Ch 5: Inside The Cell Structure of Cells • 3-D, not 2-D –spheres, cubes, or bricks –Many can change shape –Some have spikes, bulges, or other strange extensions Sizes of Cells • Vary in size –Some < ½ µm • (1 µm = 1/1000 mm or 1/1,000,000 m) –bacteria among the smallest –egg cells among the largest Why is there a limit to cell growth? 2 Main Types of Organisms • Unicellular Organisms •Multicellular Organisms –Single cell –Many cells •Carry out all processes in one cell –Ex. amoeba, paramecium, euglena •Division of labor –cells are specialized (specific functions) –Ex. You, dog, tree, elephant Why can multicellular organisms be big if there is a limit to cell size? Organization Within Cells • Why might cells need to be organized? • How are they organized??? ____________ Cell (Plasma) Membrane • Surrounds each cell – creates boundary between cell contents & outside environment (including other cells) • Acts as a gatekeeper – selectively permeable Cytoplasm • Gel-like substance filling much of cell – approx. 70% water – Contains organelles – Some chemical reactions Two Major Types of Cells • Prokaryotes – No nucleus • DNA single chromosome – no mitosis – no membranebound organelles • Eukaryotes (You – karyote!) – Nucleus • DNA multiple chromosomes – mitosis – Membrane-bound organelles Two Major Types of Cells Eukaryotic Cell Organelles • Plant & Animal Cells – – – – – – – – – – – – *Cell (plasma) membrane *Cytoplasm Nucleus Nuclear membrane (envelope) Nucleolus *Ribosome Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Bodies (Apparatus) Mitochondrion Cytoskeleton Vacuole Lysosome • Plant Cells – Chloroplast – *Cell wall • Animal Cells – *Cilia & flagella – Centrioles Nucleus • Control Center for Cell – Surrounded by nuclear membrane (envelope) • selectively permeable – Inside nucleus • Chromatin – DNA & Protein » Genetic information – Before cell divides chromatin condenses into chromosomes • Nucleolus Nucleolus • In nucleus – where RNA is produced – can have more than one Ribosomes & Endoplasmic Reticulum • Ribosomes – Synthesize proteins from amino acids – Thousands in cell • attached to endoplasmic reticulum • free in cytoplasm Ribosomes & Endoplasmic Reticulum • Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) – Network of interconnected, flattened, tube-like membranes – transport proteins through cell • Rough ER (RER) – covered w/ ribosomes • Smooth ER (SER) – Lacks ribosomes Golgi Bodies (Apparatus) • Stacks of flattened, slightly-curved, sac-shaped membranes – Packages, modifies & exports proteins within & out of cell – Lie close to ER Mitochondria • Rod-shaped – Inner membrane is highly folded • Why? • Powerhouse of the cell – Creates energy (ATP) for cell from food (glucose) • Cellular respiration Cytoskeleton • Made of microtubules & microfilaments – proteins • Give cell shape & support • Helps organelles move around cell Vacuole • Fluid-filled sac – Plant cells-large vacuole – Animal cells-small vacuoles • Store food, water, waste • Role in maintaining osmotic balance – Central vacuole • Maintains turgor pressure in plants – Contractile vacuole • Pumps water out of many unicellular freshwater protists – Why would these organisms need to pump out water? Lysosomes Lysosome animation • Small, round vesicles formed from golgi bodies – mostly in animals cells • contain digestive enzymes – break down larger food molecules – break down old, worn out cell parts Chloroplasts • Green, oval-shaped plastids w/ double-membrane – Contains chlorophyll (green pigment) • Site of photosynthesis – Makes food (glucose) & releases oxygen • Plants & some protists Chloroplast Cyclosis Cell Wall • outside cell (plasma) membrane • protection & support – made of cellulose or chitin • plants, algae, fungi, bacteria Cilia & Flagella • made from microtubules – cilia • Shorter & more numerous – flagella • Longer, but few in number • For motility (movement) – whip-like motion Centrioles • Paired, rod-like structures near nucleus – made of a cylindrical of microtubule pairs • Animal cells • play role in cell division – separate chromosome pairs during mitosis Extras • ID eukaryotic animal cell organelles: http://www.wisconline.com/Objects/ViewObject.aspx?ID=AP11 604 • Cell Part ID interactive: http://www.wisconline.com/objects/ViewObject.aspx?ID=AP114 03 • Cell Organelles Game: http://www.quia.com/mc/65947.html