* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Astronomy Review
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
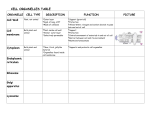
Cell Review Organelles Organelles 2 Cell Memb Plant vs OrganAnimal elles 3 Trans 1pt 1pt 1pt 1pt 1pt 1pt 2pt 2pt 2pt 2pt 2pt 2pt 3pt 3pt 3pt 3pt 3pt 3pt 4pt 4pt 4pt 4pt 4pt 4pt 5pt 5pt 5pt 5pt 5pt 5pt Organelles 1 • What organelle is responsible for containing the genetic information of the organism? • Nucleus Organelles 2 • What is the main function of the cell membrane? • Transport, Organelles 3 • What happens to a vacuole in a plant cell when there is little water available over a long period of time? What happens to the plant? (Hint: does not die) • Vacuole shrinks, cell loses rigidity. • Plant wilts Organelles 4 • What organelle is responsible for storing energy in the form of sugars? Where would this organelle be located (specific)? • Chloroplast/ Leaves Organelles 5 • What molecule makes up the cell wall in bacteria? Plants? • Peptidoglycan • Cellulose Organelles 1 • Where would you find chloroplasts in a healthy plant? (what part of the plant?) • Leaves Organelles 2 • What do all organelles have in common? • They are membrane bound Organelles 3 • What is the function of a lysosome? • Cellular digestion, breaksdown items in the cell that are no longer needed, can destroy organelles as well. Organelles 4 • What two organelles have their own DNA and ribosomes independent of the cell? • Mitochondria • Chloroplasts Organelles 5 • List in order the three organelles directly involved in protein synthesis. • Ribosomes • Endoplasmic Reticulum • Golgi Apparatus Cell Membrane 1 • What molecules are used primarily in transport? • Proteins Cell Membrane 2 • What is the function of carbohydrates on the cell membrane? • Recognition sites Cell Membrane 3 • Explain the structure of a phospholipid. How does it work as a barrier? What part is polar and non-polar? Hyprophobic and hydrophillic? Cell Membranes 4 • What 2 ions are most responsible for creating a nerve impulse? Which one is higher outside than inside under rest? Cell Membrane 5 • Can a cell wall act in place of a cell membrane? Why or why not? (think about structure) • No, cell wall is all carbohydrates so it does not allow controlled passage like a membrane Plants vs Animals 1 • What two organelles function in maintaining shape and stability in a plant cell? • Vacuole and Cell Wall Plants and Animals 2 • What is the hole (breathing) on the bottom of leaves called that is responsible for plant gas exchange? • Stomata Plant and Animals 3 • An animal cell does not have a predetermined shape. What part of the cell is responsible for support? • cytoskeleton Plants and Animals 4 • Osmosis is the passive movement of water across a membrane. In the following situation, would the water flow left of right? High Water Low Solutes High Water High Solutes Plants and Animals 5 • Blood is used in animals to transport materials through arteries and veins. What is the transport system in a plant? • xylem Organelles 3/ 1 • Where are ribosomes made? • Nucleolus Organelles 3/2 • What 3 parts are present in any living cell? Organelles 3/ 3 • What organelle requires oxygen? • Mitochondria Organelles 3/ 4 • What are 3 differences between a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell? Organelles 3/ 5 Write the chemical formula for cellular respiration. (reactants vs products) Transport • What type of molecules can pass through a membrane under normal circumstances? Transport 2 • What is the difference between diffusion and facilitated diffusion? Transport 3 • Why is a virus not considered to be a living organism? • Cannot reproduce on its own, cannot produce its own proteins, Transport 4 • What are 2 reasons a cell would use active transport to move materials across the membrane? Transport 5 • Explain endocytosis: – How it works – Why does the cell use it? What cells use it most often?