* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
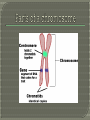
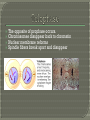
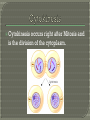
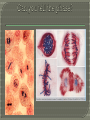
Section 10-1 & 10-2 Cells divide rather than get larger because……. 1. Demands on DNA would be too great. 2. Cell would have trouble moving food and waste across the cell membrane. Volume increases faster than surface area. Each organism has a specific number of chromosomes. During cell division chromatin condenses into chromosomes. In order for each cell to get the right number the chromosomes have to double Cell cycle – The series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide. G1 – Growth phase #1. Cells increase in size and make new proteins and organelles. S – Synthesis. Chromosomes are replicated. G2 – Growth Phase #2 Cell division organelles are produced. Short phase. Cell division is made up of 2 parts. 1. Mitosis – division of the nucleus. Divided into 4 phases. 2. Cytokinesis – division of the cytoplasm. Chromosomes are visible. Centrioles separate Spindle fibers form Nuclear membrane breaks down. Chromosomes the cell line up in the middle of Chromosomes are pulled apart/away from each other. The opposite of prophase occurs. Chromosomes disappear back to chromatin Nuclear membrane reforms Spindle fibers break apart and disappear Cytokinesis occurs right after Mitosis and is the division of the cytoplasm.