* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Organelleshlinka
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
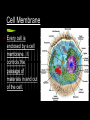
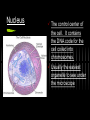
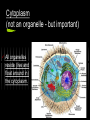
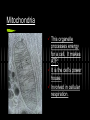
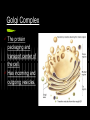
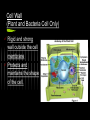
Cell Organelles What you need to know An organelle is a membranebound structure that carries out specific activities for the cell. You will need to know the following organelles and their function: Cell Membrane Nucleus Cytoplasm Mitochondria Golgi Complex Ribosomes Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Cell Wall Chloroplast Central Vacuole Lysosome Cell Membrane Every cell is enclosed by a cell membrane. It controls the passage of materials in and out of the cell. Nucleus The control center of the cell. It contains the DNA code for the cell coiled into chromosomes. Usually the easiest organelle to see under the microscope Cytoplasm (not an organelle - but important) All organelles reside (live and float around in) the cytoplasm. Mitochondria This organelle processes energy for a cell. It makes ATP. It is the cell’s power house. Involved in cellular respiration. Golgi Complex The protein packaging and transport center of the cell. Has incoming and outgoing vesicles. Ribosomes (not an organelle - but important) Synthesizes proteins. Found free floating or in Rough ER No membrane present. Made in the nucleolus Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Transports materials throughout the cell. Makes lipids QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Covered with ribosomes. Produces proteins. Transports materials throughout the cell = the “Highway” of the cell Connected to nucleus Lysosome Breaks down materials for digestion = “the Garbage Disposal” Contains special enzymes for digestion in the cell. Cell Wall (Plant and Bacteria Cell Only) Rigid and strong wall outside the cell membrane Protects and maintains the shape of the cell. Chloroplast (Plant Cell Only) Contains chlorophyll. Makes plants green. Uses light energy to make ATP & sugars. Photosynthesis takes place here. Central Vacuole (Plant Cell Only) Most plant cells have one large one. Storage container for water, food, enzymes, waste, etc. Let’s try some matching http://www.quia.com/mc/2744.html