* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download A9-Cell Parts Identification
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
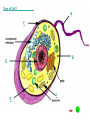
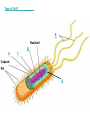
Cell Parts Labeling Game! Type of Cell? _____________ B F A E C D Type of Cell? Animal Cell Plant cells typically don’t have flagella, but plant cells do have cell walls, chloroplasts, and large central vacuoles- all of which are absent in this cell. Structure A: Cytoplasm The cytoplasm is the region between nucleus and cell membrane containing cytosol, a gel-like fluid that surrounds all cell parts and keeps them suspended in place inside the cell. Structure B: Flagella Flagella are threadlike structures that allow a cell to move by rotating and propelling the cell forward. Structure C: Mitochondria The mitochondria supplies the cell with most of its energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). This is why it is commonly called the “powerhouse” of the cell. Structure D: Ribosome Ribosomes are the smallest organelles in a cell, and they are not surrounded by a membrane. They are responsible for making proteins, or protein synthesis. Structure E: Nucleus Commonly called the “information center” or “control center” of the cell, this structure contains the cell’s instructions, or DNA. Structure F: Cell Membrane The cell membrane encloses the cell and separates the cell interior. It also plays a role in the transport of particles into and out of the cell, and cell to cell communication. Structure G: Cell Wall The cell wall is a thick layer that surrounds the cell membrane for extra protection and structural support. It is typically made of cellulose. Structure H: Chloroplast • Chloroplasts are green colored organelles that use light energy to make carbon compounds that can provide the plant with energy in a process called photosynthesis. The pigment that makes these organelles appear green is called chlorophyll. Structure I: Central Vacuole This is a large internal compartment of the cell that stores water, ions, nutrients, and waste. It also helps the plant cell keep its shape by filling up much of the empty space in the cytoplasm. Type of Cell? _____________ E D A I H G C F Type of Cell? Plant Cell This cell has a cell wall, chloroplasts, and a large central vacuole. It is also box-like in shape. These are all characteristics of a plant cell. Type of Cell? ____________ B Nucleoid D G F Capsule Pili A Type of Cell? Bacteria This is also known as a prokaryotic cell. It has no true nucleus and no membrane-bound organelles (remember, ribosomes do not have membranes around them).