* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Just Cell Organelles
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Microtubule wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
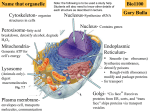
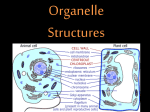
What are the 3 differences between a plant and animal cell? What does each location represent in a cell and why? ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Office Outside wall and doors to the office Principal’s office Any classroom Library Outside wall of school Doors to the school Hallways Cafeteria Boiler room Receiving area Gyms Inside walls Bathroom Organize your Notebook Look at your goals. On a separate sheet of paper write down what you have done or have not done to achieve your goals this week. How and how much did you study for the biochem test? Nucleus Nucleolus Nuclear Envelope Ribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum ◦ Smooth ◦ Rough Golgi Apparatus Vacuoles Mitochondria Microtubules Microfilaments Cell Wall Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Lysosomes Chloroplast Flagella Cilia Pick it up on the front table. Only complete the middle column. Analogy: a similarity between like features of two things, on which a comparison may be based: the analogy between the heart and a pump. The school can be used as an analogy for the cell. Based off of the school location’s function in the left hand column, give the organelle it represents in the center column (there are more than one correct answers you just need to be able to justify your answer) Plant ◦ Chloroplast ◦ Cell Wall ◦ Large Central Vacuole Animal Cell ◦ None of the above Controls functions of the cell - Houses DNA - Produces ribosomes Controls what enters and exits the nucleus Make proteins Move proteins and other substances throughout the cell Rough = Ribosomes Smooth = No Ribosomes Packaging and distribution of proteins and other chemical products to their next location Contains and removes waste products Powerhouse ATP of the cell Maintains cell shape Microtubules ◦ Proteins that give the cell its rigidity and shape ◦ Tracks for organelles to move Microfilaments ◦ Proteins that enable the cell to move or change shape Oozing movements Support and protection (plant cells and bacteria) Controls what enters and exits the cell - Cellular environment - Where most cellular activities are carried out Digests proteins, lipids and carbohydrates - Contain chlorophyll - Where photosynthesis takes place Movement Many small, hair-like projections Movement Larger whip like projections